Important
You are browsing the documentation for version 3.1 of OroCommerce, OroCRM and OroPlatform, which is no longer maintained. Read version 5.1 (the latest LTS version) of the Oro documentation to get up-to-date information.
See our Release Process documentation for more information on the currently supported and upcoming releases.
Introduction to Workflows¶
Principle¶
An entity can have assigned workflows. It means that an entity view page has a list of passed steps and allowed transition buttons. When a user clicks a button with the start transition (and submits a transition form if it exists), then in the background, a new instance of a workflow item of a specific Workflow is created.
Each step has a list of allowed transitions, and each transition has a list of conditions that define whether this transition can be performed with a specific workflow item state. If transition is allowed, then the user can perform it. If the transition has Init Actions, they are executed before the transition. If the transition has Post Actions, then these Post Actions are performed right after the transition. So, the user can move the entity through the steps of a workflow until they reach the final step where Workflow finishes.
A workflow does not always need to have the final step, and the user can perform transitions until they are allowed.
A workflow item stores all collected data and the current step, so the user can stop their progress within the workflow at any moment and then return to it - the Workflow will have exactly the same state. Each workflow item represents the workflow started for a specific entity.
Entity Limitations¶
To be able to attach an entity to a specific workflow (e.g., make an entity workflow related), a few criteria should be met.
An entity cannot have composite fields as its primary keys.
Entity primary key can be an integer or a string (for doctrine types it is: BIGINT, DECIMAL, INTEGER, SMALLINT, STRING). In other words, all types that can be casted by SQL CAST to text representation.
An entity should be configurable.
Configuration¶
All Workflow entities are described in the configuration. Below is an example of Workflow configuration that performs some action with User entity.
1 workflows:
2 example_user_flow: # name of the workflow
3 entity: Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity\User # workflow related entity
4 entity_attribute: user # attribute name of current entity that can be used in configuration
5 start_step: started # step that will be assigned automatically to new entities
6 force_autostart: false # if `start_step` is defined: force start workflow on entity creation like from cli, message queue (without any filters like applications, scopes, features)
7 steps_display_ordered: true # defines whether all steps will be shown on view page in steps widget
8 defaults:
9 active: true # active by default
10 exclusive_active_groups: [group_flow] # active only single workflow for a specified groups
11 exclusive_record_groups:
12 - unique_run # only one started workflow for the `entity` from specified groups can exist at time
13 priority: 100 # has priority of 100
14 applications: [ commerce ] # web application availability level
15 scopes:
16 - # definition of configuration for one scope
17 scopeField1: 42 # context for scope will have field `scopeField1` and entity with id `42`
18 -
19 scopeField1: 42
20 scopeField2: 3
21 scopeField3: 77
22 steps: # list of all existing steps in workflow
23 started: # step where user should enter firstname and lastname
24 order: 10 # order of step (ascending)
25 allowed_transitions: # list of allowed transition from this step
26 - set_name # first name and last name should be entered on this transition
27 processed: # step where user can review entered data
28 order: 20 # steps will be shown in ascending
29 allowed_transitions: # order of step
30 - add_email # new email should be added on this transition
31 attributes: # list of all existing attributes in workflow
32 first_name: # first name of a user
33 property_path: user.firstName # path to entity property (automatically defined attribute metadata)
34 middle_name: # middle name of a user
35 property_path: user.middleName # path to entity property (automatically defined attribute metadata)
36 last_name: # last name of a user
37 property_path: user.lastName # path to entity property (automatically defined attribute metadata)
38 email_string: # email string temporary attribute
39 type: string # attribute type
40 email_entity: # email entity temporary attribute
41 type: entity # attribute type
42 options: # attribute options
43 class: Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity\Email # entity class name
44
45 transitions: # list of all existing transitions in workflow
46 set_name: # transition from step "started" to "processed"
47 step_to: processed # next step after transition performing
48 transition_definition: set_name_definition # link to definition of conditions and post actions
49 form_options: # options which will be passed to form type of transition
50 attribute_fields: # list of attribute fields which will be shown
51 first_name: # attribute name
52 options: # list of form field options
53 required: true # define this field as required
54 constraints: # list of constraints
55 - NotBlank: ~ # this field must be filled
56 middle_name: ~ # attribute name
57 last_name: # attribute name
58 options: # list of form field options
59 required: true # define this field as required
60 constraints: # list of constraints
61 - NotBlank: ~ # this field must be filled
62 display_type: page # form will be opened in separate page
63 destination_page: index # after submitting form will be opened index page of workflow`s related entity
64 add_email: # transition from step "processed" to "processed" (self-transition)
65 step_to: processed # next step after transition performing
66 transition_definition: add_email_definition # link to definition of conditions and post actions
67 form_options: # options which will be passed to form type of transition
68 attribute_fields: # list of attribute fields which will be shown
69 email_string: # attribute name
70 options: # list of form field options
71 required: true # define this field as required
72 constraints: # list of constraints
73 - NotBlank: ~ # this field must be filled
74 - Email: ~ # field must contain valid email
75 schedule_transition: # transition from step "processed" to "processed" (self-transition)
76 step_to: processed # next step after transition performing
77 transition_definition: schedule_transition_definition # link to definition of conditions and post actions
78 triggers: # transition triggers
79 -
80 cron: '* * * * *' # cron definition
81 filter: "e.someStatus = 'OPEN'" # dql-filter
82 -
83 entity_class: Oro\Bundle\SaleBundle\Entity\Quote # entity class
84 event: update # event type
85 field: status # updated field
86 queued: false # handle trigger not in queue
87 relation: user # relation to Workflow entity
88 require: "entity.status = 'pending'" # expression language condition
89 transition_definitions: # list of all existing transition definitions
90 set_name_definition: [] # definitions for transition "set_name", no extra conditions or actions here
91 add_email_definition: # definition for transition "add_email"
92 actions: # list of action which will be performed after transition
93 - '@create_entity': # create email entity
94 class: Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity\Email # entity class
95 attribute: $email_entity # entity attribute that should store this entity
96 data: # data for creating entity
97 email: $email_string # entered email
98 user: $user # current user
99 - '@call_method': # call specific method from entity class
100 object: $user # object that should call method
101 method: addEmail # method that should be called
102 method_parameters: # parameters that will be passed to the called method
103 [$email_entity] # add email from temporary attribute
104 - '@unset_value': # unset temporary properties
105 [$email_string, $email_entity] # clear email string and entity
106 schedule_transition_definition: # definitions for transition "schedule_transition", no extra conditions or actions here
107 actions: # list of action which will be performed after transition
108 - '@assign_value': [$user.status, 'processed']# change user's status
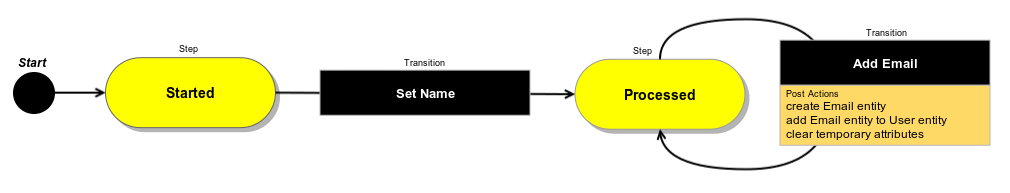
This configuration describes Workflow that includes two transitions - “set_name” and “add_email”.
On step “started”, a user can update the full name (first, middle and last name) using transition “set_name”. Then on step “processed”, the user can add additional emails using transition “add_email”.
To perform transition “set_name”, the user should fill first and last name, the middle name is optional. After this transition, the provided data is automatically set to the user through the attribute property paths. To perform transition “add_email”, the user must enter a valid email - it must not be empty and must have a valid format. This transition creates a new Email entity with the assigned email string and User entity, then adds it to the User entity to create a connection, and clears temporary attributes in last action.
There are 2 triggers that will try to perform transition schedule_transition by cron definition, or when field status of entity with class`Oro\Bundle\SaleBundle\Entity\Quote` is updated.
The following diagram shows this logic in graphical representation.
Note
If you want to test this flow in real application, you can place this configuration in file Oro/Bundle/UserBundle/Resources/config/oro/workflows.yml, reload definitions using the console command bin/console oro:workflow:definitions:load, and activate it from the UI. Next, you can go to the User view page and test it.
Console Commands¶
WorkflowBundle provides following console commands to work with workflows.
oro:workflow:definitions:load
This command loads workflow’s configurations from .yml configuration files to the database. It is used during application installation and update processes. The command has two optional options:
–directories - specifies directories used to find configuration files (multiple values allowed);
–workflows - specifies the names of the workflows that should be loaded (multiple values allowed).
Note
You must execute this command every time workflow configurations are changed in the .yml files.
oro:workflow:transit
This command performs transitions with specified name for the WorkflowItem with a specified ID. It is used to perform scheduled transitions. The command has two required option:
–workflow-item - the identifier of WorkflowItem.
–transition - the name of Transition.
oro:workflow:handle-transition-cron-trigger
This command handles workflow transition cron trigger with specified identifier. The command has one required option:
–id - identifier of the transition cron trigger.
Main Entities¶
Workflow consists of several related entities.
Step is an entity that shows the current status of the workflow. Before rendering each transitions, check if it is allowed for the current workflow item. It contains the name and the list of allowed transitions. The entity involved in the workflow has a relation to the current workflow step.
Attribute is an entity that represents one value in the workflow item, used to render the field value on a step form. Attribute knows about its type (string, object, entity etc.) and additional options. Attribute contains name.
Transition is an action that changes the current step of the workflow item (i.e., moves it from one step to another). The transition is allowed if its conditions are satisfied. Before the transition is performed, Init Actions are executed; and after the transition is performed, Post Actions are executed. A transition can be used as a start transition; it means that this transition starts the Workflow and creates a new instance of the workflow item. Transitions optionally can have a form. In this case, this form is shown to user when the transition button is clicked. The transition contains name and some additional options. Optionally, the transition can contain a form with a list of attributes.
Condition defines whether a specific transition is allowed with the specified input data. Conditions can be nested.
Actions are assigned to the transition and executed when the transition is performed. There are two kinds of actions: Init Action and Post Actions. The difference between them is that Init Actions are executed before the Transition and Post Actions are executed after the transition. Actions can be used to manage entities (create, find), manipulate attributes (e.g., assign values) and perform any other action.
Workflow aggregates steps, attributes, and transitions. A workflow is a model that does not have its own state but it can be referred by the workflow items.
Workflow Data container is aggregated by the workflow item where each value is associated with an attribute. Those values can be entered by the user directly or assigned via Actions.
Workflow Item is associated with the workflow and indirectly associated with Steps, Transitions and Attributes. It has its own state in the workflow data, the current step, and other data. The workflow item stores the entity identifier and the entity class that has an associated workflow.
TransitionTriggerEvent allows to perform a transition when during an entity event Doctrine triggers a corresponding event.
TransitionTriggerCron allows to perform a transition by cron definition.