Important
You are browsing the documentation for version 4.1 of OroCommerce, OroCRM and OroPlatform, which is no longer maintained. Read version 5.1 (the latest LTS version) of the Oro documentation to get up-to-date information.
See our Release Process documentation for more information on the currently supported and upcoming releases.
Indexation Process¶
Trigger Reindexation¶
From the Code¶
The website search index is mostly event based. The reindexation is triggered using the oro_website_search.reindexation_request event and is processed by the Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\ReindexationRequestEvent class.
This class contains the following parameters that specify the scope of the entities that have to be reindexed:
$websitesIds - list of website identifiers that should take part in the reindexation. When no IDs are provided, reindex affects all websites.
$classesNames - list of entity class names that have to be reindexed. When no classes are provided, all entities from the search index are reindexed;
$ids - list of entity identifiers that has to be reindexed. When no IDs are provided, all entities of the specified classes are reindexed;
$scheduled (default true) - boolean flag that defines whether reindexation has to be scheduled (asynchronous) or immediate (synchronous).
For example:
$websitesIds = [], $classesNames = [‘Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\Entity\Product’], $ids = [1,2,3], $scheduled = false
This combination of parameter values requests immediate reindex of the products with IDs 1, 2 and 3 for all websites (e.g. when the prices for products with IDs 1, 2, and 3 were updated).
$websitesIds = [2], $classesNames = [], $ids = [], $scheduled = true - whole search index scope (all entities)
These values call for scheduled (asynchronous) reindex of the website with ID=2, for example, after this website was created.
Sample reindexation triggered from the code:
1 use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\EventDispatcherInterface;
2 use Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\ReindexationRequestEvent;
3
4 /** @var EventDispatcherInterface $eventDispatcher */
5 $eventDispatcher = $this->container->get('event_dispatcher');
6
7 // reindexation scope - $websitesIds = [2], $classesNames = [], $ids = [], $scheduled = true
8 $event = new ReindexationRequestEvent([], [2]);
9 $eventDispatcher->dispatch(ReindexationRequestEvent::EVENT_NAME, $reindexationEvent);
From the CLI¶
Alternatively, you may trigger reindexation from the CLI using the oro:website-search:reindex command with the following optional parameters:
website-id (optional) - identifier of the website the reindexing applies to;
class (optional) - names of the entities that have to be reindexed; Note, optional only if ids option is empty
scheduled (optional) - enables indexation via the message consumers;
ids (optional) - allows entering range of entity IDs to process incl. splitting.
Below is an example of the reindex triggered via CLI:
1 > php bin/console oro:website-search:reindex --website-id=2
2 Starting reindex task for all mapped entities and website ID 2...
3 Reindex finished successfully.
Search Indexer¶
Search indexer class is responsible for putting the entity information into the search index and should implement the Oro\BundleSearchBundle\Engine\IndexerInterface interface. Default synchronous indexer is accessible via the oro_website_search.indexer service.
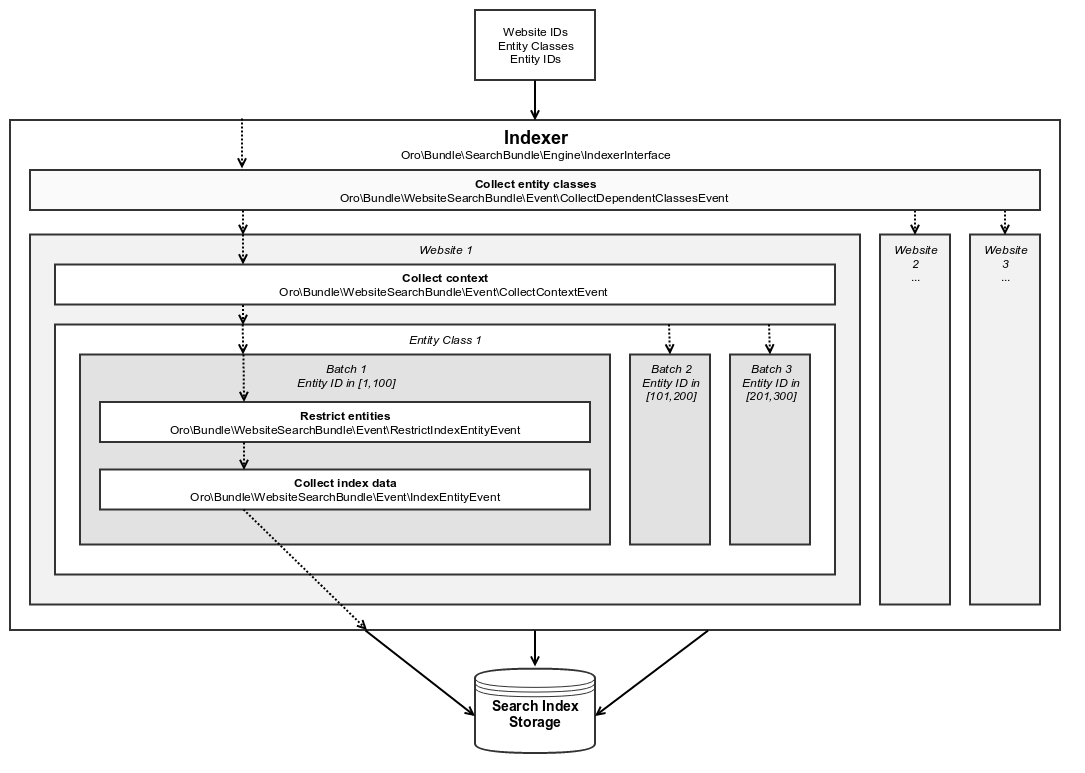
For indexation, indexer performs the following steps:
Defines the list of allowed websites and collects the list of entities that has to be indexed.
Collects current context for every website found at the first step.
Starts the indexation process for every affected entity in a scope of the specific website.
Splits indexation of the specific entity into batches by entity identifiers, collects index data and saves them in search index storage.
Search Indexer Events¶
The following sections describe events that are triggered during the indexation of data for website search:
Collect Dependent Entity Classes¶
Name: oro_website_search.event.collect_dependent_classes
Class: Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\CollectDependentClassesEvent
The event collects the list of all entity classes which have to take part in the indexation. Apart from the main entity class, the list may include other entities, e.g. indexation of customers might require indexation of orders.
Collect Context¶
Name: oro_website_search.event.collect_context
Class: Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\CollectContextEvent
The event is used to collect data that has to be consistent during the indexation. For example, the environment-related variables may change value during the indexation, but the indexation process must rely on the values that were actual when indexation started. This event is triggered for every affected website, so the environment-related variables (e.g system configuration values defined for a website) should be defined in the website scope. All the necessary data should be added to the indexation context.
Restrict Entities¶
Name: oro_website_search.event.restrict_index_entity
Class: Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\RestrictIndexEntityEvent
This event is used to restrict the list of entities that has to be stored in the search index. For example, a search should work only with the products that are enabled and are in stock. To restrict entities, add required conditions to the ORM query builder. Later it is used to retrieve entities that have to be indexed.
Collect Index Data¶
Name: oro_website_search.event.index_entity
Class: Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\IndexEntityEvent
This is the most important event because it collects the data that should be persisted to the search index. This event contains a batch of entities that have to be indexed, and you (being a developer) extract the information for the index from entities or other sources, and feed it to the event and put to the search index on the later stage. To make data collection faster and more efficient, the entities are passed in batches (default batch size is 100 entities). In most cases, you can get all the required information using just one request instead of triggering a separate request for every entity. The event also supports work with placeholders, so you can get all the related information and put it into the search index according to the specified placeholders.
Configure a New Placeholder Type¶
If you need to add another placeholder type which is not declared yet, you will need to declare it by implementing AbstractPlaceholder and register it with the website_search.placeholder tag.
1 namespace AppBundle\WebsiteSearch;
2
3 use Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Placeholder\AbstractPlaceholder;
4
5 class FooPlaceholder extends AbstractPlaceholder
6 {
7 const NAME = 'FOO_ID';
8
9 /**
10 * {@inheritDoc}
11 */
12 public function getPlaceholder()
13 {
14 return self::NAME;
15 }
16
17 /**
18 * {@inheritDoc}
19 */
20 public function getDefaultValue()
21 {
22 return '0';
23 }
24 }
1 services:
2 app.website_search.foo_placeholder:
3 class: AppBundle\WebsiteSearch\FooPlaceholder
4 tags:
5 - { name: website_search.placeholder }
Asynchronous Search Indexer¶
The website search supports two types of indexation: immediate (synchronous) and scheduled (asynchronous). Regular indexer works synchronously, so you have to wait until indexation is finished. Asynchronous indexer sends a message to the Message Queue to process it later by workers.
Default asynchronous indexer is implemented in the Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Engine\AsyncIndexer class and is accessible via the oro_website_search.async.indexer service. To trigger asynchronous indexation, set $scheduled parameter to true.
Asynchronous indexer is using Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Engine\AsyncMessaging\ReindexMessageGranularizer to split message per entity and websiteId. What the request message granularizer does:
on 1 indexation request message to handle entity Product within all websites [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] it splits the message into 5 different smaller messages, that allows handling each Product entity with each websiteId separately
on messages that contain large amounts of entityIds, it splits entityIds table into smaller chunks, for example 1000 entityIds will be split into 10 messages with 100 entityIds each
For each message Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Engine\AsyncMessaging\SearchMessageProcessor builds jobs with unique names to avoid parallel reindexation of same sets of entities, and runs them unique performing actual reindexation. In case, no parameters have been passed (empty class and context), the job will NOT be run as unique.
Asynchronous indexer can send messages with the following topics:
oro.website.search.indexer.save - save list of specified entities to the search index;
oro.website.search.indexer.delete - delete list of specified entities from the search index;
oro.website.search.indexer.reset_index - reset (clear) the entire index or a specific entity class in it;
oro.website.search.indexer.reindex - reindex the entire index or a specific part of it.
Example¶
Let’s assume that you have the following index structure and want to index the product data:
1 Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\Entity\Product:
2 alias: oro_product_WEBSITE_ID
3 fields:
4 -
5 name: sku
6 type: text
7 -
8 name: names_LOCALIZATION_ID
9 type: text
10 -
11 name: all_text_LOCALIZATION_ID
12 type: text
13 store: false
14 -
15 name: all_text
16 type: text
17 store: false
Below is an example of the index listener for the index structure above:
1 use Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\Entity\Product;
2 use Oro\Bundle\WebsiteBundle\Provider\AbstractWebsiteLocalizationProvider;
3 use Oro\Bundle\WebsiteBundle\Provider\WebsiteLocalizationProvider;
4 use Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\IndexEntityEvent;
5 use Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Manager\WebsiteContextManager;
6
7 class WebsiteSearchProductIndexerListener
8 {
9 /**
10 * @var WebsiteContextManager
11 */
12 private $websiteContextManager;
13
14 /**
15 * @var WebsiteLocalizationProvider
16 */
17 private $websiteLocalizationProvider;
18
19 /**
20 * @param AbstractWebsiteLocalizationProvider $websiteLocalizationProvider
21 * @param WebsiteContextManager $websiteContextManager
22 */
23 public function __construct(
24 AbstractWebsiteLocalizationProvider $websiteLocalizationProvider,
25 WebsiteContextManager $websiteContextManager
26 ) {
27 $this->websiteLocalizationProvider = $websiteLocalizationProvider;
28 $this->websiteContextManager = $websiteContextManager;
29 }
30
31 /**
32 * @param IndexEntityEvent $event
33 */
34 public function onWebsiteSearchIndex(IndexEntityEvent $event)
35 {
36 // get current website ID
37 $websiteId = $this->websiteContextManager->getWebsiteId($event->getContext());
38 if (!$websiteId) {
39 $event->stopPropagation();
40 return;
41 }
42
43 // get all entities that have to be indexed
44 /** @var Product[] $products */
45 $products = $event->getEntities();
46
47 // get all localizations of the current website
48 $localizations = $this->websiteLocalizationProvider->getLocalizationsByWebsiteId($websiteId);
49
50 // iterate over entities that have to be indexed
51 foreach ($products as $product) {
52 // add non localized field to search index
53 $event->addField($product->getId(), 'sku', $product->getSku(), true);
54
55 // add localized field to search index
56 foreach ($localizations as $localization) {
57 $event->addPlaceholderField(
58 $product->getId(),
59 'names_LOCALIZATION_ID',
60 (string)$product->getName($localization),
61 ['LOCALIZATION_ID' => $localization->getId()],
62 true
63 );
64 }
65 }
66 }
67 }
Service declaration for such listener might look like the following example:
1 services:
2 oro_product.event_listener.website_search_index:
3 class: Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\EventListener\WebsiteSearchProductIndexerListener
4 arguments:
5 - '@oro_website.provider.website_localization'
6 - '@oro_website_search.manager.website_context_manager'
7 tags:
8 - { name: kernel.event_listener, event: oro_website_search.event.index_entity.product, method: onWebsiteSearchIndex }
This listener has two dependencies: a AbstractWebsiteLocalizationProvider (usually represented by the oro_website.provider.website_localization service) and a WebsiteContextManager (usually represented by the oro_website_search.manager.website_context_manager service). The listener uses the oro_website_search.event.index_entity.product event name, and the product suffix means that this listener is called only for the product indexation. To call a method for all entities, use the event without suffix (oro_website_search.event.index_entity).
First, indexation method extracts website ID from the context. If the website is not found (e.g. it was removed or became not accessible), indexation stops. Otherwise, the method gets the list of products from the event and the list of localizations for the current website. Finally, the required data is extracted from entities and is added to the event.
To add plain data without a placeholder, handle the event by calling the addField method. Pass the following information: identifier of the entity (required), field name (required), field value (required) and whether this value should appear in all_text fields (optional, default false).
To add data with a placeholder, handle the by calling the addPlaceholderField method for every data combination that has to be stored in a search index. The method accepts identifier of the entity (required), field name (required), field value (required), the list of placeholders with their values (required ) and a flag that states whether this value should appear in all_text fields (optional, default false).
Let’s assume that Oro application has two websites and two localizations:
Global website (ID=1) supports two localizations (English ID=1 and Russian ID=2);
Russian website (ID=2) supports one localization (Russian ID=2).
And here is what search index might contain after the indexation:
oro_product_1
1 {
2 1: {
3 sku: "PR1",
4 names_1: "First product",
5 names_2: "Первый продукт",
6 all_text_1: "PR1 First product",
7 all_text_2: "PR1 Первый продукт",
8 all_text: "PR1 First product Первый продукт"
9 },
10 2: {
11 sku: "PR2",
12 names_1: "Second product",
13 names_2: "Второй продукт",
14 all_text_1: "PR2 Second product",
15 all_text_2: "PR2 Второй продукт",
16 all_text: "PR2 Second product Второй продукт"
17 }
18 }
oro_product_2
1 {
2 1: {
3 sku: "PR1",
4 names_2: "Первый продукт",
5 all_text_2: "PR1 Первый продукт",
6 all_text: "PR1 Первый продукт"
7 },
8 2: {
9 sku: "PR2",
10 names_2: "Второй продукт",
11 all_text_2: "PR2 Второй продукт",
12 all_text: "PR2 Второй продукт"
13 }
14 }
Values in all all_text fields are generated automatically based on the values of all fields passed to search index.