Important
You are browsing documentation for version 5.0 of OroCommerce, supported until January 2025. Read the documentation for version 6.0 (the latest LTS version) to get up-to-date information.
See our Release Process documentation for more information on the currently supported and upcoming releases.
Advanced Configuration
Deployment and Maintenance Configuration
To modify configuration options for maintenance agent, you need to have the orocloud.yaml file placed in the application root. If the application is not yet deployed, modifications can also be made in /mnt/(ocom|ocrm)/app/orocloud.yaml.
The validation command checks your configuration for syntax errors or wrong configuration values. Use the files argument to check custom files or multiple files merge result:
orocloud-cli config:validate
orocloud-cli config:validate /mnt/ocom/app/orocloud.yaml
orocloud-cli config:validate /mnt/ocom/app/www/orocloud.yaml
orocloud-cli config:validate /mnt/ocom/app/orocloud.yaml /mnt/ocom/app/www/orocloud.yaml
orocloud-cli config:validate /mnt/ocom/app/orocloud.yaml /mnt/ocom/app/www/orocloud.yaml /mnt/ocom/app/www/orocloud_prod.yaml
Valid changes are applied within 40 minutes or automatically during deployments.
Use the help command to get configuration details or configuration reference:
orocloud-cli config:help
orocloud-cli config:help webserver.limit_whitelist
orocloud-cli config:help orocloud_options.webserver.limit_whitelist
Note
Please do not use double quotes for any variables. Use single quotes instead.
Note
Please do not use tabs in orocloud.yaml as indentations as they are treated differently by different editors and tools. Since indentation is crucial for proper interpretation of YAML, use spaces only.
With orocloud.yaml it is possible to override the following nodes:
install_commands
Hint
See the oro:install command description for more information.
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
install_commands: # Application commands which run during the installation process
- 'oro:install --sample-data=n --user-name=admin --user-email=admin@example.com --user-password=new_password --user-firstname=John --user-lastname=Doe --application-url=https://example.com --organization-name=Oro'
Note
As most of time the deploy operation runs only once, it is recommended to avoid storing any sensitive data (such as email, username, or password) in any files for security purposes. You can omit options like user-name, user-email or user-password. When omitted, they are asked interactively during the deploy operation.
upgrade_commands
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
upgrade_commands: # Application commands which run during update process
- 'oro:platform:update'
git clone configuration
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
git_clone_recursive: true
Note
Please note that by default, git_clone_recursive: true. Allowed values: true, false.
composer_command
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
composer_command: '{{composer_cmd}} install --no-dev --optimize-autoloader'
Note
Please note that {{composer_cmd}} is a reserved variable and in most cases during executions it will be replaced with the composer value. Please, keep in mind that the command format is IMPORTANT and should take the following form: {environment variables} {{composer_cmd}} {command} {option1 option2 ... option n}.
For example:
{{composer_cmd}} install –no-dev -vvv
COMPOSER=dev.json {{composer_cmd}} install –no-dev -vvv
Some options may also be omitted as they are added automatically:
The –working-dir (-d) option will be ignored because it is added automatically during the deploy | upgrade command.
The –no-interaction (-n) option will be ignored because it is added automatically during the deploy | upgrade command.
The -v|vv|vvv, –verbose option will be used (if specified) with a higher priority than the same option in the deploy | upgrade command, e.g.
orocloud-cli deploy -vv.
after_composer_install_commands
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
after_composer_install_commands:
- 'command1'
db_extensions
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
db_extensions:
- 'uuid-ossp'
- 'pgcrypto'
before_backup_create_commands
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
before_backup_create_commands:
- 'command1'
- 'command2'
after_backup_create_commands
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
after_backup_create_commands:
- 'command1'
- 'command2'
Application Configuration
There are two types of pages in OroCloud, maintenance and error. Maintenance pages allow to determine the page you will see when you move the application into the maintenance mode. Error pages allow to redefine the standard pages that will be displayed in the event of the following errors:
Error 403 can be returned by the application itself when authorization is blocked, and by the web application firewall.
Note
This status also can also be returned by nginx when the requested URL is forbidden or by the OroCommerce application itself. These pages are mananged by ngnix and the application respectively.
Error 451 appears when requests are blocked by the firewall if they do not fit access policy, for example, when a request is coming from a forbidden IP address (see OroCloud WAF Configuration section for more information)
Error 501 is returned when when service is not implemented and/or the application does not support the requested functionality
Error 502 is returned when the server is unavailable (for example, because of the outage).
error_pages_path is a dynamic error page directory configuration. The default location is the error_pages directory in a repository. File matching works with response codes and hosts, like 503.$host.html => 503.html => error_pages option value. Supported response codes are 403, 451, 501, 502, and 503.
Custom maintenance pages, error pages (403, 451, 501, 502), error pages path, web backend prefix, and consumer debug mode can be configured as described below. Keep in mind that the web_backend_prefix parameter must start with “/” but never end with “/” (for instance, ‘/admin’):
---
orocloud_options:
application:
maintenance_page: 'public/maintenance.html'
error_pages:
403: 'public/403.html'
451: 'public/451.html'
501: 'public/501.html'
502: 'public/502.html'
error_pages_path: 'error_pages'
web_backend_prefix: '/my_admin_console_prefix'
consumers_debug_mode: true
The maintenance_page, error_pages_path and error_pages are relative paths to files in the application repository. When modified, changes are applied after the deploy | upgrade operation in approximately 40 minutes.
Note
Changing the web_backend_prefix value without notifying the Cloud team can break the back-office of the application. Make sure you create a request to the Service Desk before making any changes. You can also change the value without creating a request. In this case, you should wait for approximately 30 min and then, run upgrade:source to apply changes.
Webserver Configuration
Webserver configuration can be modified, as illustrated below:
---
orocloud_options:
webserver:
header_x_frame: true
header_x_frame_app_control: true
redirects_map:
'/about_us_old': '/about'
'/about_them_old': '/about_them'
'/news/new_event' : 'https://corpsite.com/events/newest'
redirects_map_include:
- 'redirects/website1.yml'
- 'redirects/website2.yaml'
- '/mnt/ocom/app/redirects.yml'
locations:
'root':
type: 'php'
satisfy: any # Allow access if all (all) or at least one (any) access directive satisfied
location: '~ /index\.php(/|$)'
auth_basic_enable: true
auth_basic_userlist:
user1:
ensure: 'present'
password: 'password1'
user2:
ensure: 'absent'
password: 'password2'
'admin':
type: 'php'
satisfy: any # Allow access if all (all) or at least one (any) access directive satisfied
location: '~ /index\.php(/admin|$)'
auth_basic_enable: true
auth_basic_userlist:
user3:
ensure: 'present'
password: 'password1'
user4:
ensure: 'absent'
password: 'password2'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
'de':
type: 'php'
location: '/de'
fastcgi_param:
'WEBSITE': '$host/de'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
'en':
type: 'php'
location: '/en'
fastcgi_param:
'WEBSITE': '$host/en'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
access_policy:
'ip':
'type' : 'allow'
'allow' :
- '127.0.0.1'
- '192.168.0.1'
- '172.16.0.0/16'
'deny' :
- '10.0.0.1'
'country':
'type' : 'deny'
'allow' :
- 'US'
- 'CA'
'ua':
'allow' :
- 'GoogleStackdriverMonitoring'
- 'Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/5.0); 360Spider',
- 'Mozilla\/5\.0 \(compatible\;\ MSIE\ 9\.0;\ Windows\ NT 6\.1\;\ Trident\/5\.0\)\;\ 360Spider',
'deny' :
- 'AcoiRobot'
- 'Wget'
'uri':
'allow' :
- '~(^/api/(.*))'
limit_whitelist:
- '8.8.8.8'
- '10.1.0.0/22'
limit_whitelist_uri:
- '~(^/admin/test/(.*))'
blackfire_options:
agent_enabled : true
apm_enabled : 1
server_id : '<server-id>'
server_token : '<server-token>'
log_level : '1'
log_path : '/var/log/blackfire/agent.log'
newrelic_options:
license_key: ‘shaike5fith3ieKahn4zae6iedeiphoo7Phoo1ca’
Redirects Configuration
This configuration option enables you to set up redirects to the existing URLs of OroCloud application.
redirects_map — the hash where the key is an old URL, and the value is a new URL.
redirects_map_include — list of YAML files with the hashes where the key is an old URL, and the value is a new URL (similar to
redirects_map).
X Frame Header Configuration
header_x_frame: true — is the default value of the flag. In this case, OroCloud WAF adds the “X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN” header when responding to the initial request. It makes it impossible to embed any OroCommerce site into iFrame at any site except itself to fulfill security requirements.
header_x_frame_app_control: true - Ignore “X-Frame-Options” header and allow application to decide if header is required.
Some business cases require embedding the OroCloud site into the iFrame at other sites. You need to set the value to “false” : header_x_frame: false.
This prevents WAF from sending the “X-Frame-Options” header which allows embedding into any iFrame.
Locations Configuration
This configuration option is used to manage locations.
locations — the hash of hashes. The top key is the location name; the lower keys are:
type — location type. Possible values are
php,static,rewrite.satisfy — defines how conditions are used. Possible values are
allandany.all - all conditions must be met for the specific location (logical
and)any - any condition can be met for the specific location (logical
or)
location — location URI. The value may have regular expressions and modifiers, as it is used in the Nginx location directive.
fastcgi_param — the hash for php-specific custom variables.
auth_basic_enable — a boolean trigger for HTTP basic authentication.
auth_basic_userlist — the hash of hashes with a user name as a key and mandatory nested keys:
ensure — ensures if the user is present or absent.
password — a plain text user password.
allow — an array of IP addresses or network masks allowed to access location. Use one record per line or
anyto allow access from anywhere.deny — an array of IP addresses or network masks denied to access location. Use one record per line or
anyto deny access from anywhere.
OroCloud WAF Configuration
Approach
OroCloud provides two ways to protect the application from big amounts of requests which can cause denial of service. There are two layers of protection used by the OroCloud application which are illustrated in the diagram below:
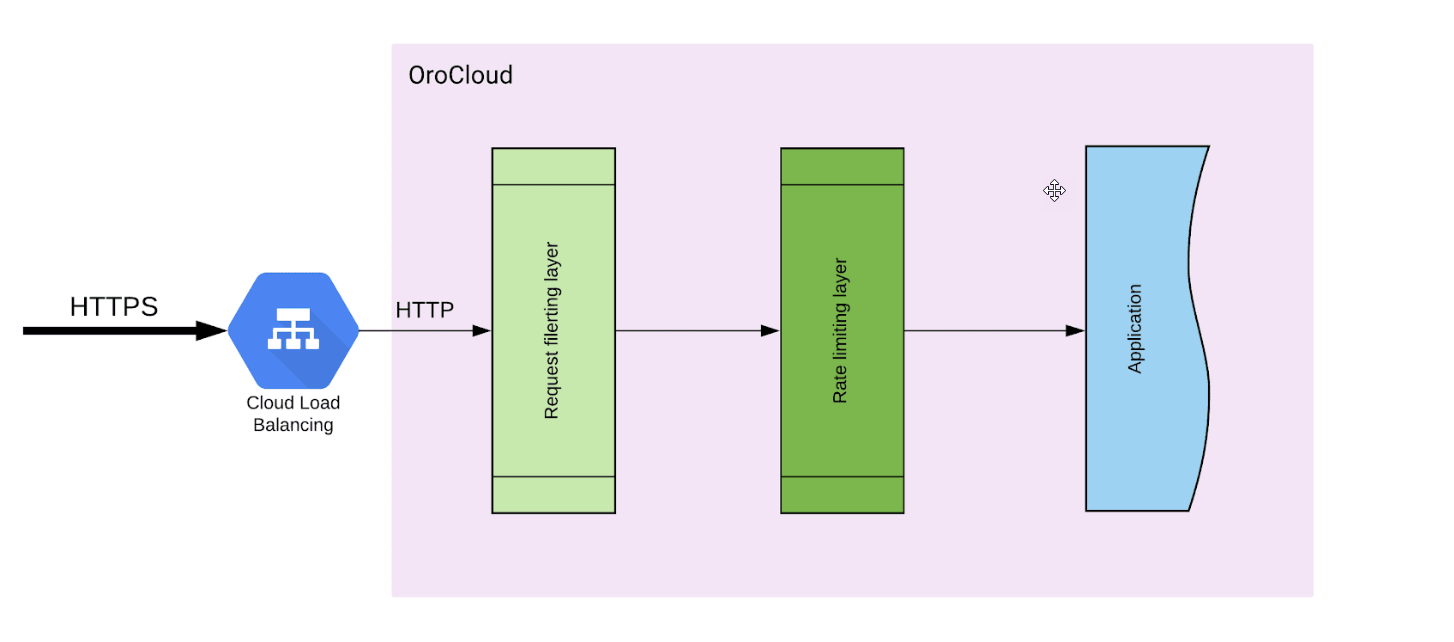
Requests Filtering
This layer is responsible for filtering HTTP requests depending on their sources. The requests can come from certain:
IP addresses or networks
Countries
User Agents
The rules used by this firewall are defined in the access_policy section of the orocloud.yaml file and are explained below. The HTTP request dropped at this layer of protection has HTTP status 451 which is “Unavailable For Legal Reasons”.
Robot Detection
The application drops requests from the user agents which do not support JS effectively protecting from the simple robots. Any request from a client (browser, robot, etc.), which do not support cookies and JS, is dropped with HTTP status 451, and this client is redirected to the error page. It is possible to whitelist specific user agents using the rules described below.
Rate Limiting Request
On this layer, WAF performs rate limiting to detect crawling robots and excessive HTTP requests using the following mechanisms.
Rate limiting algorithm uses 3 parameters: rate limit, delay, and burst. It groups requests by the source IP and destination URI and throttles them to the rate limit if there are more than a delay requests per second for a given group of requests. Nginx drops all consequent requests from a group if their amount is bigger than the burst value. The exact values of these parameters depend on the grouping factor (IP, URI, etc.).
HTTP request dropped at this layer of protection has HTTP status 451 “Unavailable For Legal Reasons”. It is possible to define exceptions for rate limiting using the limit_whitelist and limit_whitelist_uri sections of the orocloud.yaml file.
Rules Definition
WAF Rules
Rules to manage HTTP requests filtering are defined in the following sections of the orocloud.yaml file.
Before implementing changes in this file on production, you should always test it at the environment stage to avoid issues with live application.
Source filtering rules are defined in the webserver section. This is the child element of the orocloud_options data structure. Here is an example of rules definitions:
---
orocloud_options:
webserver:
access_policy:
'ip':
'type' : 'allow'
'allow' :
- '127.0.0.1'
- '192.168.0.1'
- '172.16.0.0/16'
'deny' :
- '10.0.0.1'
'country':
'type' : 'deny'
'allow' :
- 'US'
- 'CA'
'ua':
'allow' :
- 'GoogleStackdriverMonitoring'
- 'Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Trident/5.0); 360Spider',
- 'Mozilla\/5\.0 \(compatible\;\ MSIE\ 9\.0;\ Windows\ NT 6\.1\;\ Trident\/5\.0\)\;\ 360Spider',
'deny' :
- 'AcoiRobot'
- 'Wget'
'uri':
'allow' :
- '~(^/api/(.*))'
access_policy — The hash of hashes provides the ability to manage Oro Web Application Firewall and allow or deny requests depending on the source address, source country, user agent, and URI.
All rejected requests receive status 451.
The following hashes can be used:
ip— the hash defines the rules for the source IP filtering.country— the hash defines rules for the originating country filtering. The value of type key defines if the hash contains the allowed or prohibited countries. Country must be defined by ISO 3166 Alpha1 code. GeoIP database is used to define a country from the source IP.
An example of the rule to allow only the defined countries:
'country':
'type' : 'deny'
'allow' :
- 'US'
- 'CA'
In this example, only the requests from the USA and Canada are allowed. All other requests are rejected.
An example of the rule to deny requests from the defined countries:
'country':
'type' : 'allow'
'deny' :
- 'CN'
- 'RU'
In this example, all requests from China and Russia are to be rejected.
ua— The hash provides the ability to allow or deny requests from the specific user agents. A user agent is defined by the regexp string. Scalar values are transformed to regexps automatically. There are two possible lists for this hash:allowanddenyto allow or deny requests from the listed user agents.
An example of the user agent rule:
'ua':
'allow' :
- 'GoogleStackdriverMonitoring'
- 'AdsBot-Google (+http://www.google.com/adsbot.html)'
'deny' :
- 'AcoiRobot'
- 'Wget'
This example allows requests from the GoogleStackdriverMonitoring and AdsBot-Google user agents and rejects all requests from AcoiRobot and Wget.
uri— The hash provides the ability to allow requests to the specific URI and override the rules defined by other hashes inaccess_policy. URI can be defined by standard regexp.
An example of the URI rule:
'uri':
'allow' :
- '~(^/api/(.*))'
This example allows any requests to the URI which fits ~(^/api/(.*)) regex overriding any rule defined for IP, country, and/or user agent.
Request Rate Limit Rules
There are two lists to allow any rate of requests for the specific IPs or to the specific URIs. They are the child elements of the webserver data structure.
Here is an example:
limit_whitelist:
- '8.8.8.8'
- '10.1.0.0/22'
limit_whitelist_uri:
- '~(^/admin/test/(.*))'
limit_whitelist — The list contains source IPs and subnets which are allowed to send requests to the application with any rate. This can be used to whitelist some service IPs which need to perform many requests, e.g., for load testing.
An example of the whitelist:
limit_whitelist:
- '8.8.8.8'
- '10.1.0.0/22'
This rule allows unlimited rate of requests from IP 127.0.0.1 (local host) and subnet 10.1.0.0/22.
limit_whitelist_uri — The list contains regular expressions to define URI of the application which must not be limited by request rate. This can be used to whitelist URIs that need to receive many requests, e.g., integration URI.
An example of the whitelist:
limit_whitelist_uri:
- '~(^/admin/test/(.*))'
This rule allows the unlimited rate of requests to URI containing the /admin/test/ string.
Note
Allowing access via WAF does not affect simultaneous connections limits. Use limit_whitelist or limit_whitelist_uri to set unlimited connectios for a client IP or URI on the server.
Domain Configuration
webserver-like configuration per domain:
orocloud_options:
domains:
oro-cloud.com:
locations_merge: true
maintenance_page: 'public/oro-cloud.html'
header_x_frame_app_control: true
redirects_map:
'/about_us_old': '/about'
'/about_them_old': '/about_them'
redirects_map_include:
- 'redirects/website1.yml'
- 'redirects/website2.yaml'
- '/mnt/ocom/app/redirects.yml'
locations:
'de':
type: 'php'
location: '/de'
fastcgi_param:
'WEBSITE': '$host/de'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
'en':
type: 'php'
location: '/en'
fastcgi_param:
'WEBSITE': '$host/en'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
example.com:
locations_merge: false
maintenance_page: 'public/example.html'
header_x_frame_app_control: true
redirects_map:
'/about_us_old': '/about'
'/about_them_old': '/about_them'
redirects_map_include:
- 'redirects/website3.yml'
- 'redirects/website4.yaml'
- '/mnt/ocom/app/redirects.yml'
locations:
'root':
type: 'php'
satisfy: any # Allow access if all (all) or at least one (any) access directive satisfied
location: '~ /index\.php(/|$)'
auth_basic_enable: true
auth_basic_userlist:
user1:
ensure: 'present'
password: 'password1'
user2:
ensure: 'absent'
password: 'password2'
'admin':
type: 'php'
satisfy: any # Allow access if all (all) or at least one (any) access directive satisfied
location: '~ /index\.php(/admin|$)'
auth_basic_enable: true
auth_basic_userlist:
user3:
ensure: 'present'
password: 'password1'
user4:
ensure: 'absent'
password: 'password2'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
'de':
type: 'php'
location: '/de'
fastcgi_param:
'WEBSITE': '$host/de'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
'en':
type: 'php'
location: '/en'
fastcgi_param:
'WEBSITE': '$host/en'
allow:
- '127.0.0.1'
- '127.0.0.2'
deny:
- 'all'
Profiling Application Console Commands via Blackfire
The configuration option enables you to configure Blackfire.
blackfire_options — The hash is used to configure the Blackfire agent on environment
agent_enabled — a boolean trigger for Blackfire installation
apm_enabled - the option enables (1) or disables (0) the Blackfire APM feature. Please note that you need to have it included into your license.
server_id — a server ID string. Refer your Blackfire account to this value.
server_token — a server token string. Refer your Blackfire account to this value.
log_level — Blackfire agent log verbosity.
log_path — a path to the log file location.
You can then profile the application console commands via configured Blackfire:
orocloud-cli app:console [command] --blackfire-enable --blackfire-client-id [client-id] --blackfire-client-token [client-token] [--blackfire-env env] [--blackfire-samples count]
Note
Make sure you enable Blackfire via orocloud.yaml before using this functionality.
Profiling Application Using NewRelic
The newrelic_options configuration option allows you to configure NewRelic profiler (must be installed and configured per separate support request). Please, pay attention that the value of the license_key is provided as an example, and you need to use your actual license key there.
Mail Settings
To prevent sending test emails accidentally from the staging environment to any real users or customers, add the domains of email recepients that you will be using for testing to your whitelist:
---
orocloud_options:
mail:
whitelist:
- 'example.com'
- 'examlpe.org'
- 'example.net'
Where:
mail is a hash of mail-related settings
whitelist is an array of whitelisted mail domains
Note
In production environments all domains are whitelisted. When you create a whitelist, it blocks sending email to any recipients, except for the ones in the whitelisted email domains.
Sanitizing Configuration
Regardless of application type (OroCommerce or OroCRM), each has its own default sanitize rules (sanitize.method.rawsql and sanitize.method.update). However, you can add your own rules, remove a specific default rule, or completely override them.
The sanitize configuration is grouped under the sanitize node and supports the following sanitize methods:
sanitize.rawsql_add_rules — the list of raw SQL queries that helps you to sanitize the existing data, for example, delete data using the TRUNCATE method, UPDATE data to apply any custom modification, etc.
sanitize.rawsql_delete_rules — the list of raw SQL queries, which should be removed from the list in sanitize.method.rawsql. The format is the same as sanitize.rawsql_add.
sanitize.rawsql_override_rules — the list of raw SQL queries, which will be applied to sanitizing data and override default sanitize rule sanitize.method.rawsql. Please note, that if this option is specified, all sanitize.rawsql_add_rules and sanitize.rawsql_delete_rules will be ignored. The format is the same as sanitize.rawsql_add_rules.
sanitize.update_add_rules — the mapping between specific table columns and the sanitizing method that should be used for the values.
sanitize.update_delete_rules — the list of rules which will be deleted from the list in sanitize.method.update. The format is the same as in sanitize.update_add_rules.
sanitize.update_override_rules — the list of rules which will be applied to sanitizing data and overriding the default sanitize rule sanitize.method.update. Please note, that if this option is specified, all sanitize.update_add_rules and sanitize.update_delete_rules will be ignored. The format is the same as sanitize.update_add_rules.
Note
Please keep in mind that ALL values in rawsql_*_rules and update_*_rules MUST be wrapped in SINGLE quotes.
---
orocloud_options:
deployment:
sanitize:
rawsql_add_rules:
- 'TRUNCATE oro_message_queue_job_unique_test'
rawsql_delete_rules:
- 'TRUNCATE oro_tracking_visit_event'
- 'TRUNCATE oro_tracking_website CASCADE'
rawsql_override_rules:
- 'TRUNCATE oro_tracking_visit_event'
- 'TRUNCATE oro_tracking_website CASCADE'
update_add_rules:
- '{ table: oro_email_test, columns: [{name: subject, method: md5}, {name: from_name, method: md5}] }'
update_delete_rules:
- '{ table: oro_integration_transport, columns: [{name: api_key, method: md5},{name: api_user, method: md5},{name: api_token, method: md5}] }'
update_override_rules:
- '{ table: oro_integration_transport, columns: [{name: api_key, method: md5},{name: api_user, method: md5},{name: api_token, method: md5}] }'
custom_email_domain: 'example.com'
General Conventions
Please use the following conventions to design your sanitize.update_* strategy:
Provide sanitizing configuration for every table as a new item:
update_add_rules: - '{ table: oro_address, columns: [{name: street, method: md5}, {name: city, method: md5}, {name: postal_code, method: md5}, {name: last_name, method: md5}] }' - '{ table: oro_business_unit, columns: [{name: email, method: email}, {name: name, method: md5}, {name: phone, method: md5}] }'Provide the table name in the table node.
In the columns section, provide an array of column name and sanitizing method pairs for all the columns that should be sanitized in the mentioned table.
For example:
columns: [{name: street, method: md5}, {name: city, method: md5} ]Provide the column name in the name node. Use the following sanitize methods/strategies (ensure they reasonably match the column type):
md5 — Replaces the original string with the string hash.
email — Replaces the email with the sanitized version of the email. When the sanitize.custom_email_domain configuration parameter is provided in the deployment.yml or orocloud.yaml files, the email strategy replaces the real email domain with the custom one provided as sanitize.custom_email_domain. If the custom domain is not provided, the sanitized email will be generated randomly. For example, example@example.com.
date — Replaces the date values with the current date and time.
attachment — Replaces the attachment file content with a dummy blank image.
Elasticsearch Synonyms Configuration
Note
Please avoid simultaneous use of search synonyms and the method of adding synonyms described in this article, as this will lead to unpredictable behavior.
To configure synonyms in Elasticsearch service, use the following field in orocloud.yaml:
orocloud_options:
elasticsearch:
synonyms:
'index_name1':
- 'foo, bar, baz'
- 'spam, eggs, meal'
- 'null, void'
'index_name2':
- 'Alice, Bob, Dave, John'
You can use separate synonym lists for each index, or use ‘*’ as index name in order to apply the same synonyms list to all indices.
orocloud_options:
elasticsearch:
synonyms:
'*':
- 'foo, bar, baz'
- 'spam, eggs, meal'
- 'null, void'
- 'Alice, Bob, Dave, John'
Note
Please keep in mind that synonyms configuration will be not applied immediately. All changes made in orocloud.yaml require up to 40 minutes to apply. More details for synonyms usage may be found in official Elasticsearch documentation.
Environments Data Synchronization
Cloud-based environments may be synchronized by a user without filing a request to the support team.
To retrieve a list of the environments to which you can sync the sanitized data from the current environment, run the following command:
orocloud-cli dump:environments
Note
If you have no environments in the output, ask the support team to update your environment settings.
This means that you can push data from the current environment to the linked environment.
orocloud-cli dump:create --help
Description:
Create application environment data dump and copy it to another environment.
Usage:
dump:create [options]
Options:
--log=LOG Log to file
--downtime-duration[=DOWNTIME-DURATION] (OPTIONAL) Downtime duration, by default 1 hour. Expected format: '{number}d{number}h{number}m'. Usage example: '1d3h15m' means 1 day 3 hours 15 minutes OR '30m' means 30 minutes.
--downtime-comment[=DOWNTIME-COMMENT] Comment for provided custom downtime value. Required if [downtime-duration] provided. Wrap with double-quotes if contains spaces.
-e, --environment[=ENVIRONMENT] Name of the destination environment where data dump will be copied. To list all available environments, please use dump:environments command.
-c, --components[=COMPONENTS] Comma-separated components list (without spaces) to be included in the dump. Allowed: db,ess,media,code. Default: db. Database is sanitized. If media component selected, it may take much time. [default: "db"]
-i, --indices[=INDICES] Comma-separated Elastic indices list to be included in the dump. If not set - all indices will be included.
-h, --help Display this help message
-q, --quiet Do not output any message
-V, --version Display this application version
--ansi Force ANSI output
--no-ansi Disable ANSI output
-n, --no-interaction Do not ask any interactive question
-v|vv|vvv, --verbose Increase the verbosity of messages: 1 for normal output, 2 for more verbose output and 3 for debug
* **option "--environment"** - Name of the destination environment where data dump will be copied.
* **option "--components"** - Comma-separated components list (without spaces) to be included in the dump. Allowed: db,ess,rpm. Default: db. Database is sanitized.
* **option "--indices"** - Comma-separated Elastic indices list to be included in the dump. If not set - all indices will be included.
Note
RabbitMQ messages sync is not supported. If media component is selected, sync may take a long time.
When data push is done, you may start with import in the target environment.
To list all available data dumps that can be restored to the current environment, run:
orocloud-cli dump:list --help
Description:
Lists all available data dumps that can be restored to the current environment.
Usage:
dump:list [options]
Options:
--log=LOG Log to file
--page=PAGE Page for display (25 items per page) [default: 1]
--per-page=PER-PAGE Items per page [default: 25]
-h, --help Display this help message
-q, --quiet Do not output any message
-V, --version Display this application version
--ansi Force ANSI output
--no-ansi Disable ANSI output
-n, --no-interaction Do not ask any interactive question
-v|vv|vvv, --verbose Increase the verbosity of messages: 1 for normal output, 2 for more verbose output and 3 for debug
To restore it as is, run the following command in the target environment:
orocloud-cli dump:load --help
Description:
Load application data from the dump to the current environment.
Usage:
dump:load [options] [--] [<timestamp>]
Arguments:
timestamp The timestamp of the exported environment list items to be restored.
Options:
--log=LOG Log to file
--downtime-duration[=DOWNTIME-DURATION] (OPTIONAL) Downtime duration, by default 1 hour. Expected format: '{number}d{number}h{number}m'. Usage example: '1d3h15m' means 1 day 3 hours 15 minutes OR '30m' means 30 minutes.
--downtime-comment[=DOWNTIME-COMMENT] Comment for provided custom downtime value. Required if [downtime-duration] provided. Wrap with double-quotes if contains spaces.
--force[=FORCE] Force dump:load operation execution, otherwise the confirmation will be requested. [default: false]
--host[=HOST] Stop program(s) on specified job host only [ocom-vdrizheruk-dev2-app1], otherwise [all].
-c, --components[=COMPONENTS] Comma-separated list (without spaces) of components for data to be loaded. Allowed: db,ess,media,code. Default: db. Database is sanitized. If media component selected, it may take much time.
--skip-purge-media Skip purging media on fetch operation
--skip-prepare-app Skip prepare application operations. With this option application will not be usable after finishing operation.
--flush-elasticsearch Flush ElasticSearch. All ElasticSearch data will be lost.
--run-base-reindex Run command [oro:search:reindex] in background.
--run-website-reindex Run command [oro:website-search:reindex] in background.
-h, --help Display this help message
-q, --quiet Do not output any message
-V, --version Display this application version
--ansi Force ANSI output
--no-ansi Disable ANSI output
-n, --no-interaction Do not ask any interactive question
-v|vv|vvv, --verbose Increase the verbosity of messages: 1 for normal output, 2 for more verbose output and 3 for debug
* **option "--components"** - Comma-separated list (without spaces) of components for data to be loaded. Allowed: db,ess,rpm. Default: db. Database is sanitized.
* **option "--skip-prepare-app"** - Skip prepare application operations. With this option application will not be usable after finishing operation.
* **option "--flush-elasticsearch"** - Flush ElasticSearch. All ElasticSearch data will be lost.
* **option "--run-base-reindex"** - Run command [oro:search:reindex] in background to update search index for the specified entities.
* **option "--run-website-reindex"** - Run command [oro:website-search:reindex] in background to rebuild storefront search index.
Note
If during dump:load not all components(db,ess,rpm) are selected, the application may be not working. By default only db will be restored.
Note
During dump:load, the database is always sanitized.