Important
You are browsing upcoming documentation for version 7.0 of OroCommerce, scheduled for release in 2026. Read the documentation for the latest LTS version to get up-to-date information.
See our Release Process documentation for more information on the currently supported and upcoming releases.
Action Groups
Action Group is a named block of execution logic grouped under its own actions configuration node. Action groups can be called along with the @run_action_group action in any application configuration node that Action Component supports. The Action group declaration also has an important configuration section - parameters that describes all the data expected to obtain from the caller (with a type, requirement, default value, and validation message).
Parameters are accessible in actions as the root node of contextual data (e.g., $.parameterName). Along with parameters and actions, you can also optionally declare a special acl_resource criteria and a custom conditions node where you can define special instructions to check against before the bunch execution process.
Action Group Configuration
action_groups: # root node for action groups
demo_flash_greetings_to: # name of action group
replace: # (optional) the list of nodes that should be replaced during the overriding
- actions # node name
parameters: # parameters declaration node
what: # name of the parameter
type: AcmeDemoBundle/String/Phrase # (optional, default = any) type validation of parameter (available types: integer, string, boolean, array, double, object, PHP class)
message: "Bad type" # (optional) message to be prompted if parameter validation failure met
default: "Hello" # (optional) default value for optional parameter, if not set then parameter `what` is required
who: ~ # set all defaults to parameter options (type: any)
conditions: # Condition expression
'@not_empty': [ $.who ]
actions: # list of actions that should be executed
- '@call_service_method':
service: type_guesser
method: guess
method_parameters: [ $.who ] # as you can see, parameters are accessible from root $.<parameterName>
attribute: $.typeOfWho
- '@flash_message':
message: '$.result[message]'
type: 'info'
message_parameters:
param1: $.what
param2: $.typeOfWho
Next, run this action_group as follows:
@run_action_group:
action_group: demo_flash_greetings_to
parameters_mapping:
who: $.myInstanceWithVariousType
Here, we skip the what parameter, which has the default value.
To see the @run_action_group`syntax, please refer to :ref:`the actions section <bundle-docs-platform-action-bundle-action-component>.
Data Isolation
Note that Action group runs with empty context data. For example, if a caller context is mapped with parameters_mapping to a new context (under @run_action_group), action group is executed along with it. In this case, there will only be the data supported by the action group parameters declaration. This is why action groups can be called from different places and under various circumstances.
Call from PHP
All named action groups are internally gathered under the oro_action.action_group_registry registry service which is the instance of the Oro\Bundle\ActionBundle\Model\ActionGroupRegistry class. It has simple api to get the action group configured instance and perform its execution by applying the \Oro\Bundle\ActionBundle\Model\ActionGroup::execute method with proper parameters.
Recommendations
User Interface
In the above-mentioned actions block, we have used the action called @flash_message for example purposes. Usually, you do not perform any user interface-related actions in the action group actions set, as they are called or used only in the scope of the actions with no user interface environment available in runtime.
Using Results of Action Group
`ActionInterface` implements most actions and stores the results of these actions under their execution context object. Usually, it is one of the `AbstractStorage` child instances. So all the results of the action group are accessed from the context data passed to its execute(…) method.
Here, there are two @run_action_group configuration options: results (transfers data from the action group context to the caller context separately) and result (allocates all context of the executed action group under a desired node of the caller context).
Hint
See Actions for more information about @run_action_group options.
Exposing Service as Action Group
Action Group is a simple way to expose some logic to YAML that can be used by other Action Groups, Actions, or Workflows. However, at some point, supporting complex logic in YAML may require too much effort. To improve the maintainability of the logic, the developer may consider moving the logic from the action group to a service and use all the advantages of writing code in PHP. Another possible use case is to make an existing service method available as an action group.
action_groups:
prettify_string:
service: acme.demo.useful_functions
method: prettifyString
return_value_name: pretty_string
parameters:
input_string:
service_argument_name: input
In the example above, the prettifyString method of the acme.demo.useful_functions service was exposed as action group named prettify_string with input method argument mapped as input_string action group parameter. By default, all method parameters are exposed as action group parameters using PHP Reflection with their types and default values. return_value_name is configured to map the method return value correctly to the action data context.
The call_service_method action can be used instead of exposing the service method as an action group, and it is up to the developer which syntax to use. At the same time, action group services are quite useful to keep backward compatibility when some complex logic has been considered to be moved to PHP and can still be called from different places as an action group.
Action Group Events
The platform provides several events that are triggered at various points in the action group lifecycle. These events allow developers to hook into the execution process and execute custom logic at specific points in the action group. This is particularly useful for adding additional business logic, sending notifications, or updating external systems based on action group activity. Special guard event can be used to prevent the action group from being executed.
Available Events
oro_action_group.guard
Validate whether the action group is allowed. This is a guard event.
The two events being dispatched are:
oro_action_group.guard
oro_action_group.[action group name].guard
oro_action_group.pre_execute
An action group logic is starting execution (triggered right before the execution of action group actions).
The two events being dispatched are:
oro_action_group.pre_execute
oro_action_group.[action group name].pre_execute
oro_action_group.execute
An action group logic is being executed (triggered right after execution of action group actions).
The two events being dispatched are:
oro_action_group.execute
oro_action_group.[action group name].execute
Action Executor Helper
When considering moving an action group to PHP, its logic may depend on existing actions and conditions that can’t simply be called from PHP because of their tight coupling to the action/expression component architecture and execution context. To simplify this transition, the Oro\Bundle\ActionBundle\Model\ActionExecutor helper has been added. It simplifies the execution of existing actions, action groups, and evaluation of expression conditions by providing the following methods:
public function executeAction(string $actionName, array $data = []): mixed;
public function executeActionGroup(string $actionGroupName, array $data = []): ActionData;
public function evaluateExpression(
string $expressionName,
array $data = [],
\ArrayAccess $errors = null,
string $message = null
): bool;
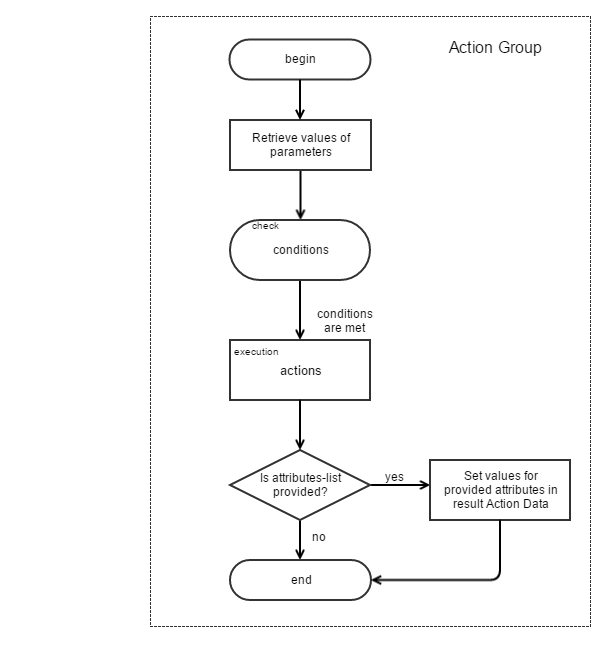
Action Group Diagram
The following diagram shows the logic of the action group process in graphical representation: