Important
You are browsing the documentation for version 4.1 of OroCommerce, OroCRM and OroPlatform, which is no longer maintained. Read version 5.1 (the latest LTS version) of the Oro documentation to get up-to-date information.
See our Release Process documentation for more information on the currently supported and upcoming releases.
Localization¶
Localization is the process of translating and adapting a product for a specific country or region. OroPlatform allows a user to customize the format of date/time/datetime, numeric and percent values, monetary values as well as the format of names and addresses.
System Configuration¶
The OroPlatform system configuration which is available in the System > Configuration menu has a special Localization section that defines localization parameters.
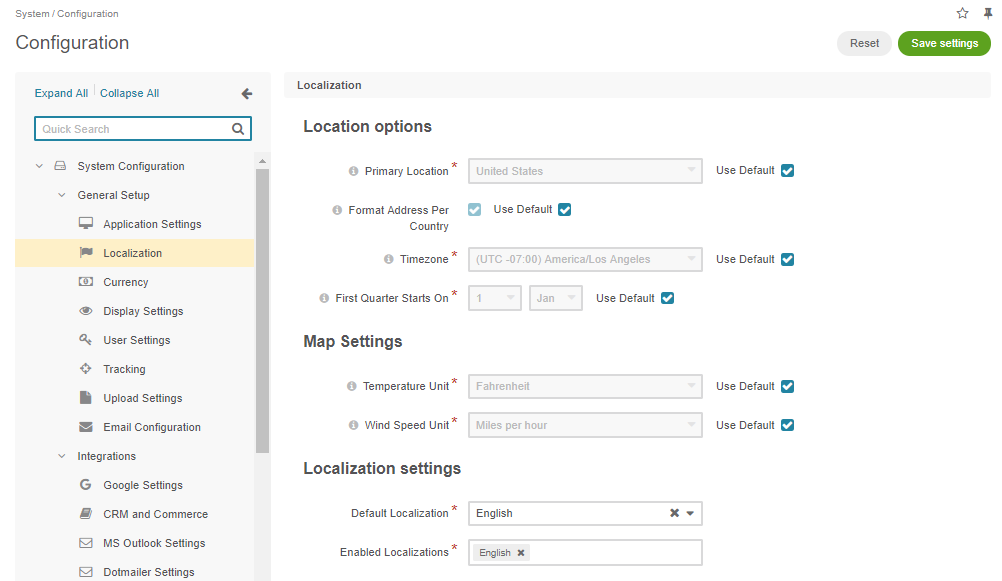
Primary Location: usually refers to the current country and is used to define appropriate address formats and the default currency;
Format address per country: is a flag used to define whether or not an address should be formatted according to the rules of its country, or if the primary location of the application should be used instead;
First Quarter Starts on: defines the first day of the first quarter. This value is used to generate proper reports;
Timezone: defines which timezone should be used to render time and datetime values;
Temperature Unit and Wind Speed Unit are used to render additional information on location maps.
Default Localization: specifies the default language of the back-office and storefront UI.
Enabled Localizations: provides the list of localizations generated automatically based on the data preconfigured in the System > Localization > Localizations menu.
Configuration Files¶
Localization information is stored in configuration files. Each bundle can
add its own localization information using appropriate files (each has to
be stored in the bundle’s Resources/config/oro directory):
locale_data.yml¶
1# Resources/config/oro/locale_data.yml
2US:
3 currency_code: USD
4 phone_prefix: '1'
5 default_locale: en_US
6RU:
7 currency_code: RUB
8 phone_prefix: '7'
9 default_locale: ru
This file contains the most basic information for countries (US and RU
are country codes as defined by ISO 3166). Each country configuration provides
information about a country’s currency (according to ISO 4217), the phone
number prefix (as defined in E.164) and its default locale (e.g. the locale
that is used to define the appropriate name format by country for specific
address).
name_format.yml¶
1# Resources/config/oro/name_format.yml
2en: "%prefix% %first_name% %middle_name% %last_name% %suffix%"
3ru: "%last_name% %first_name% %middle_name%"
This file specifies a name format per locale. Allowed placeholders are:
%prefix%%prefix%%first_name%%middle_name%%last_name%%suffix%
address_format.yml¶
1# Resources/config/oro/address_format.yml
2US:
3 format: "%name%\n%organization%\n%street%\n%CITY% %REGION_CODE% %COUNTRY_ISO2% %postal_code%"
4RU:
5 format: "%postal_code% %COUNTRY% %CITY%\n%STREET%\n%organization%\n%name%"
This file specifies the name format for addresses and, optionally, some additional address information. Each placeholder can be lowercased (data will be rendered as is) or uppercased (data will be rendered in upper case).
The allowed placeholders are:
%name%%street%%city%%country%%country_iso2%%country_iso3%%region%%region_name%%region_code%%postal_code%%organization%
Date and Numeric Formatting¶
Both dates and numbers (decimal, percent or currency) are formatted using INTL library functions. Therefore, this library is required and dates and numbers are formatted according to the installed version of the library.
The application provides formatter services that can be used to format dates and numbers in the backend which are actually simple wrappers for the INTL library:
Oro\Bundle\LocaleBundle\Formatter\DateTimeFormatterformatDate()formatTime()format()
Oro\Bundle\LocaleBundle\Formatter\NumberFormatterformatDecimal()formatPercent()formatCurrency()formatSpellout()formatDuration()formatOrdinal()
These formatter methods can be used in twig templates as filters:
oro_format_dateoro_format_timeoro_format_datetimeoro_format_numberoro_format_currencyoro_format_decimaloro_format_percentoro_format_spelloutoro_format_durationoro_format_ordinal
For example, the following Twig template prints a formatted datetime and a formatted monetary value:
1{{ entity.createdAt|oro_format_datetime }}
2{{ item.value|oro_format_currency }}
Supposed that the current locale is en and that USD is the currency
being used, the template will render the following values:
1May 28, 2014 1:40 PM
2$5,103.00
In addition to backend formatters, the application also provides the following similar formatters on the frontend side which are powered by JavaScript and can be accessed using JS modules aliases:
orolocale/js/formatter/datetime(datetime.js)formatDate(value)formatTime(value)formatDateTime(value)
orolocale/js/formatter/number(number.js)formatDecimal(value)formatInteger(value)formatPercent(value)formatCurrency(value)
Name Formatting¶
Some entities in the application may have names that require localization before they’re rendered. Localization includes the formatting of name parts according to a specified format (see name_format.yml).
On the backend side, such an entity must implement the
Oro\Bundle\LocaleBundle\Model\FullNameInterface.
This interface contains methods to extract all parts of a name, including
the name prefix, the first name, the middle name, the last name and the name
suffix. Furthermore, there are separate interfaces for each name part that
can be used when an entity defines only a subset of the full name definition.
Formatting is done on backend side by applying the
Oro\Bundle\LocaleBundle\Formatter\NameFormatter::format method
from the Oro\Bundle\LocaleBundle\Formatter\NameFormatter class.
It receives an entity and returns it as string which is formatted according
to the defined rules.
The same formatting can be used in twig templates using the oro_format_name
filter:
1{{ entity|oro_format_name }}
For the en locale, an entity implementing the FullNameInterface will
be formatted like this:
1Mr. John S Doe Jr.
On the frontend side, the same formatting can be performed with the orolocale/js/formatter/name
JS module which is located in Oro/Bundle/LocaleBundle/Resources/public/js/formatter/name.js.
This module has a similar format() method which can be used to format
a person object.
Address Formatting¶
Other entities may represent addresses that should be appropriately formatted when being rendered. The application provides a list of default address formats for several countries (see address_format.yml).
Further, an address entity may have person fields and implement the FullNameInterface
interface. In this case, the name will be rendered according to the country’s
default locale and will be used instead of an appropriate placeholder.
To support formatting, an address entity should implement the
Oro\Bundle\LocaleBundle\Model\AddressInterface which defines
methods to retrieve all required address parts (street, city, region name/code,
postal code, country name/ISO2/ISO3 and organization).
The backend formatter, Oro\Bundle\LocaleBundle\Formatter\AddressFormatter,
provides a format()
method which returns a string representation of an address that can include
default newline separators (\n).
To use this formatter in a template, use the oro_format_address filter:
1{{ address|oro_format_address }}
When used with the USA, such an address will be rendered like so:
1Mr. Roy K Greenwell
2Products Inc.
32413 Capitol Avenue
4ROMNEY IN US 47981
As with other entities, the frontend provides an appropriate JavaScript formatter,
the orolocale/js/formatter/address JS module. This module is located
in the address.js file in the Locale bundle and contains a format()
method which behaves exactly like the backend formatter does.