Important
You are browsing documentation for version 5.1 of OroCommerce, supported until March 2027. Read the documentation for the latest LTS version to get up-to-date information.
See our Release Process documentation for more information on the currently supported and upcoming releases.
Perform Search
Hint
See the Search Index documentation to get a more high-level understanding of the search index concept in the Oro application.
Search Engine
Search engine is an entry point in the Oro application that is used to perform search request. Search engine implements Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Engine\EngineInterface interface with one method - search(Query $query, array $context = []).
This method accepts a low level query object (Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\QueryQuery), sends a request to the search engine and returns result object (Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\QueryResult). The $context variable may be used to pass additional parameters specific for the search engines. A default website search engine is accessible via the oro_website_search.engine service.
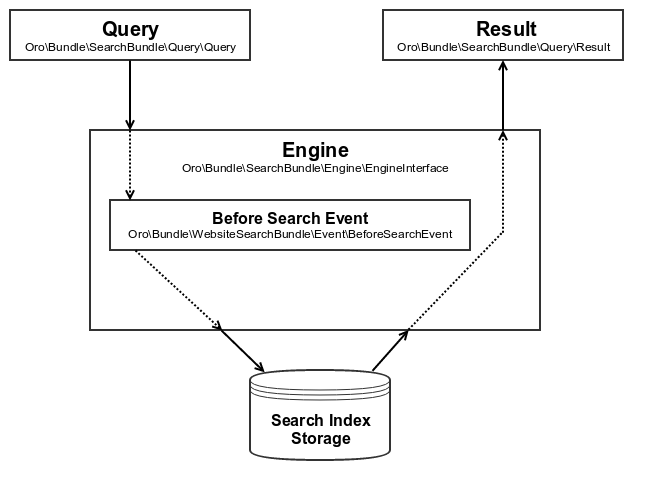
Every engine may have its own requests to modify the way request is sent. However, every engine should support the Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Event\BeforeSearchEvent out of the box. This event is triggered before the engine queries the search index storage, so the developer can check request parameters and modify the query according to the business logics.
The event name - oro_website_search.before_search - can be used to add a new listener.
Here is an example of such listener definition:
services:
oro_product.product_visibility_restriction_listener:
class: Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\EventListener\ProductVisibilityRestrictionListener
arguments:
- '@oro_product.product.manager'
- '@oro_website_search.provider.search_mapping'
tags:
- { name: kernel.event_listener, event: oro_website_search.before_search, method: process }
Search Query
Developer may start constructing a search query by adjusting the Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Query example.
Let’s assume there is a product entity with the following index structure:
Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\Entity\Product:
alias: oro_product
fields:
-
name: sku
type: text
-
name: name
type: text
-
name: price
type: decimal
and you want the following query to be executed:
SELECT
text.sku,
text.name,
decimal.price
FROM
oro_product
WHERE
text.name ~ product
ORDER_BY
decimal.price ASC
The following example illustrates how to build and execute such a query:
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Query;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Result;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Criteria\Criteria;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Engine\EngineInterface;
$query = new Query();
$query
->addSelect(['text.sku', 'text.name', 'decimal.price'])
->from('oro_product');
$query->getCriteria()
->andWhere(Criteria::expr()->contains('text.name', 'product'))
->orderBy(['decimal.price' => Query::ORDER_ASC]);
/** @var EngineInterface $engine */
$engine = $this->getContainer()->get('oro_website_search.engine');
/** @var Result $engine */
$result = $engine->search($query);
Where the $result variable is an Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Result object that contains collection of Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Result\Item objects. Every object in the collection contains information about an entity involved in a search query: entity class, entity ID and additional selected data.
This type of query is used when the search engine and its configuration is unknown, and you need an instance of an engine which implements Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Engine\EngineInterface.
As a universal, search-engine agnostic solution, you may use the Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Query\WebsiteSearchQuery that implements the Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\SearchQueryInterface interface. This type does not require additional search-engine-specific parameters and can be used in components that should be able to work with any search engine. Basically, such query encapsulates previous type of query and the required parameters to perform search (in this case it is a search engine).
To create the latter type of query, you can use specific factory for website search, or use the generic one and specify the index you used:
$query = $this->container->get('oro_website_search.query_factory')->create();
// OR
$query = $this->container->get('oro_search.query_factory')->create(['search_index' => 'website']);
Let’s execute the request to the search index mentioned above using second type of query:
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\SearchQueryInterface;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Result;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Criteria\Criteria;
/** @var SearchQueryInterface $query */
$query = $this->container->get('oro_website_search.query_factory')->create();
$query
->addSelect(['text.sku', 'text.name', 'decimal.price'])
->setFrom('oro_product')
->addWhere(Criteria::expr()->contains('text.name', 'product'))
->setOrderBy('decimal.price', Query::ORDER_ASC);
/** @var Result $engine */
$result = $query->getResult();
As you can see, the interface is similar, but you are not aware about search engine and index type that is used. This information is resolved on the factory level, so you can override and decorate the service that represents the factory to customize search behavior.
Note
There is a hard limit of 1000 on quantity of results which search query can return.
Search Repository
To store custom queries that are used to receive data from the search index, SearchBundle provides the search repository class – Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\SearchRepository – with default logic. The WebsiteSearchBundle extends this class and adds Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Query\WebsiteSearchRepository. The only difference between these repositories is the type of index that is used. Basic repository uses default index from SearchBundle, and the website search repository uses website search index.
You may want to use website repository to create a specialized repository for an entity in the website search index. Similar to the Doctrine object repository, you can use this one to store the website search related methods.
Let’s have a look at the example of such repository:
namespace Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\Search;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Criteria\Criteria;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Query;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\Result;
use Oro\Bundle\SearchBundle\Query\SearchQueryInterface;
use Oro\Bundle\WebsiteSearchBundle\Query\WebsiteSearchRepository;
class ProductRepository extends WebsiteSearchRepository
{
/**
* @param string $string
* @return Result
*/
public function findByAllText($string)
{
/** @var SearchQueryInterface $query */
$query = $this->createQuery();
$query
->addSelect(['text.sku', 'text.name', 'decimal.price'])
->addWhere(Criteria::expr()->contains('text.name', $string))
->setOrderBy('decimal.price', Query::ORDER_ASC);
return $query->getResult();
}
}
This is exactly the same query described before encapsulated in the repository. No need to call the factory methods. Define this repository as a service and use it wherever you need it.
Below is an example of search repository service declaration:
services:
oro_product.website_search.repository.product:
parent: oro_website_search.repository.abstract
class: Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\Search\ProductRepository
calls:
- [setEntityName, ['Oro\Bundle\ProductBundle\Entity\Product']]
Parent oro_website_search.repository.abstract service already contains all required constructor arguments. You may specify the entity name to automatically fill the FROM part of the query. This call is optional. If it is missing, an empty query will be created.