Actions
The action is a set of processors that handle a request.
Each action has two required elements:
context - An object that stores the input and output data and shares data between processors.
main processor - The main entry point for an action. This class is responsible for creating the context and executing all worker processors.
For more details about these elements, see the Creating a New Action section.
The following table shows all actions provided out-of-the-box:
Action Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Returns an entity by its identifier. |
|
Returns a list of entities. |
|
Deletes an entity by its identifier. |
|
Deletes a list of entities. |
|
Creates a new entity. |
|
Updates an existing entity. |
|
Updates a list of entities of the same type. |
|
Returns a list of related entities represented by a relationship. |
|
Updates an entity or entities (depending on the association type) connected to an entity to which the sub-resource belongs. This action does not have the default implementation, additional processors should be added for each sub-resource |
|
Adds an entity or entities (depending on the association type) connected to an entity to which the sub-resource belongs. This action does not have a default implementation, additional processors should be added for each sub-resource. |
|
Deletes an entity or entities (depending on the association type) connected to an entity to which the sub-resource belongs. This action does not have the default implementation, additional processors should be added for each sub-resource. |
|
Returns relationship data. |
|
Updates the “to-one” relationship and completely replaces all members of the “to-many” relationship. |
|
Adds one or several entities to a relationship. This action is applicable only to “to-many” relationships. |
|
Deletes one or several entities from a relationship. This action is applicable only to “to-many” relationships. |
|
Returns communication options for a resource. |
|
Makes modifications to the data loaded by the get, get_list and get_subresource actions. |
|
Makes modifications to and validation of the submitted data, and entities to be persisted into the database by the create, update, update_relationship, add_relationship and delete_relationship actions. |
|
Returns the configuration of an entity. |
|
Returns metadata of an entity. |
|
Converts a value to a requested data type. |
|
Returns a list of all resources accessible through the API. |
|
Returns a list of all sub-resources accessible through the API for a given entity type. |
|
Builds a response for the case when a request does not match any public action, e.g., when the HTTP method is not supported for the REST API request. |
|
Builds a response for the case when an unexpected error happens before any public action is started. |
|
Used by the update_list action to update/create a set of entities of the same type. |
|
Used by the batch_update action to update/create an entity that is part of a batch operation. |
See the Processors section for more details on creating a processor.
You can use the oro:api:debug command to display the list of all available actions and processors.
Public Actions
get Action
This action is intended to retrieve an entity by its identifier. For more details, see the Fetching Data section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_item.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}.
The HTTP method for REST API: GET.
The context class: GetContext. Also see Context class for more details.
The main processor class: GetProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.get.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug get to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
To add a new processor to this group, include it to the security_check group of actions that execute this action. For example, compare with the security_check group of the create or update actions. |
build_query |
Building a query required to load the data. |
– |
load_data |
Loading data. |
Use the customize_loaded_data action to modify loaded data. |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
Use the same rules as for the security_check group to add a new processor to this group. |
normalize_data |
Converting the loaded data into an array. |
In most cases, the processors from this group are skipped because the EntitySerializer loads most entities and returns already normalized data. For details, see LoadEntityByEntitySerializer. |
finalize |
Final validation of the loaded data and addition of the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
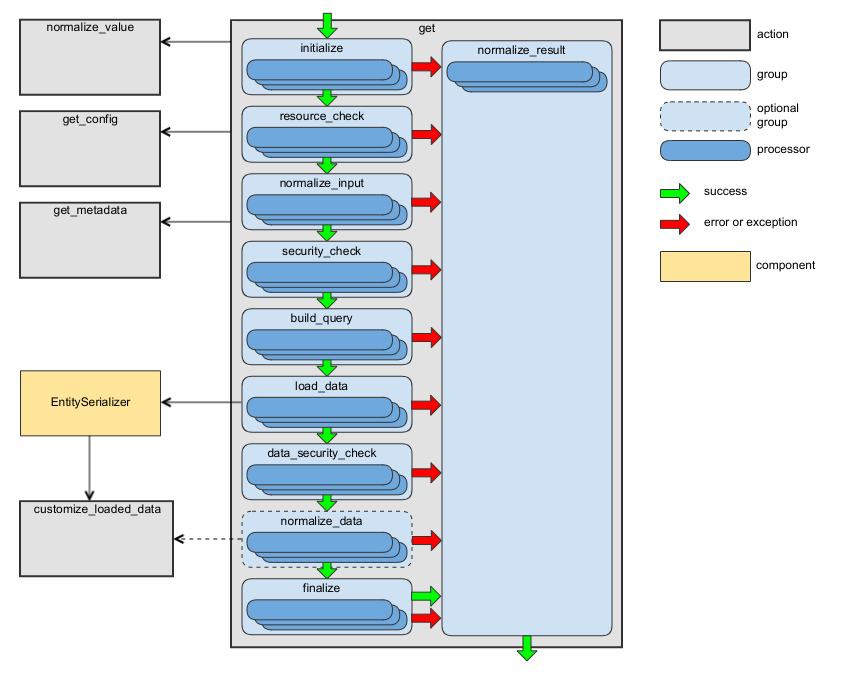
See the handleGet method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
get_list Action
This action retrieves a list of entities. For more details, see the Fetching Data section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_list.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}.
The HTTP method for REST API: GET.
The context class: GetListContext. Also see Context class for more details.
The main processor class: GetListProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.get_list.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug get_list to list the processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
build_query |
Building a query required to load data. |
– |
load_data |
Loading data. |
Use the customize_loaded_data action to modify loaded data. |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
normalize_data |
Converting the loaded data into an array. |
In most cases, the processors from this group are skipped because the EntitySerializer loads most entities and returns already normalized data. For details see LoadEntitiesByEntitySerializer. |
finalize |
Final validation of the loaded data and adding required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from one of the previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
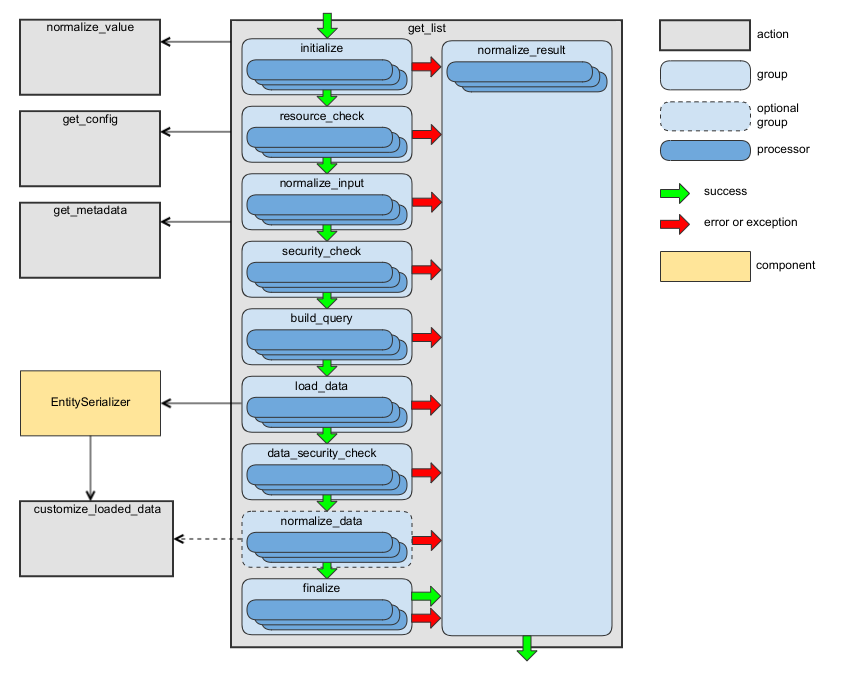
See the handleGetList method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
delete Action
This action deletes an entity by its identifier. For more details, see the Deleting Resources section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_item.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}.
The HTTP method for REST API: DELETE.
The context class: DeleteContext. Also see Context class for more details.
The main processor class: DeleteProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.delete.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug delete to list the processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading an entity to be deleted. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
delete_data |
Deleting an entity. |
– |
finalize |
Adding required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if any processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
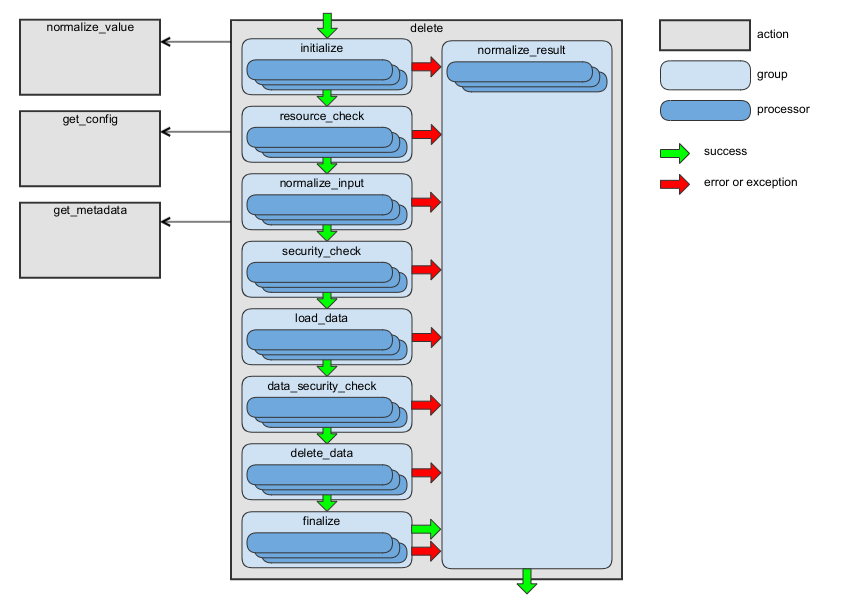
See the handleDelete method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
delete_list Action
This action deletes a list of entities.
The entities list is built based on input filters. You must specify at least one filter, otherwise, you will get an error.
By default, the maximum number of entities that can be deleted by one request is 100, see the max_delete_entities option in General Configuration. This limit minimizes the impact on the server. You can change this limit for an entity in Resources/config/oro/api.yml but test it carefully as a higher limit can significantly impact the server. See an example of changing the default limit in the How To topic.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_list.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}.
The HTTP method for REST API: DELETE.
The context class: DeleteListContext. See the Context class for more details.
The main processor class: DeleteListProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.delete_list.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug delete_list to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
build_query |
Building a query that loads a list of entities to be deleted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading the list of entities to be deleted. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
delete_data |
Deleting the list of entities. |
– |
finalize |
Adding required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:

See the handleDeleteList method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
create Action
This action creates a new entity. For more details, see the Creating Resources section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_list.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}.
The HTTP method for REST API: POST.
The context class: CreateContext. See Context class for more details.
The main processor class: CreateProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.create.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug create to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
If you add your own security processor in the security_check group of the get action, add it to this group as well. It is required because the VIEW permission is checked here: the created entity should be returned in the response, and the security_check group of the get action is disabled by oro_api.load_normalized_entity processor. |
load_data |
Creating a new entity object. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
Use the same rules as for the security_check group to add a new processor to this group. |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
Use the customize_form_data action to modify and validate submitted data and entities to be persisted into the database. |
normalize_data |
Converting created entity into array. |
– |
finalize |
Adding required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. Processors from this group are not executed for 4. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
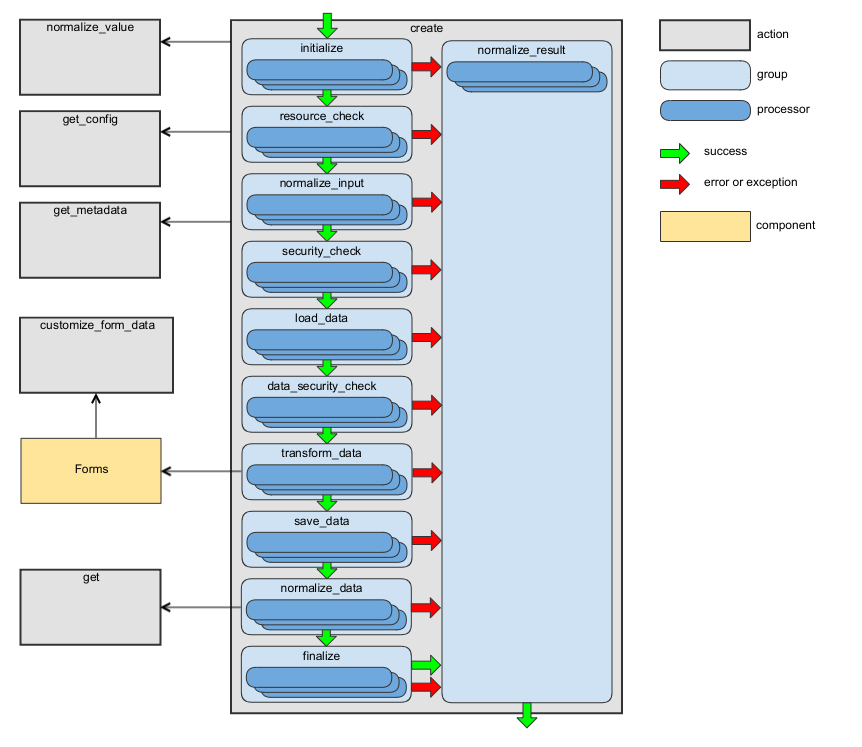
See the handleCreate method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
update Action
This action updates an entity. For more details, see the Updating Resources section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_item.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}.
The HTTP method for REST API: PATCH.
The context class: UpdateContext. Also see Context class for more details.
The main processor class: UpdateProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.update.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug update to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource is granted. |
When you add a new processor to the security_check group of the get action, add it to this group as well. This is necessary because the VIEW permission is checked here: the updated entity should be returned in the response, and the security_check group of the get action is disabled by the oro_api.load_normalized_entity processor. |
load_data |
Loading an entity object to be updated. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
Use the same rules as for the security_check group to add a new processor to this group. |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
Use the customize_form_data action to modify and validate submitted data, and entities to be persisted into the database. |
normalize_data |
Converting updated entity into an array. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
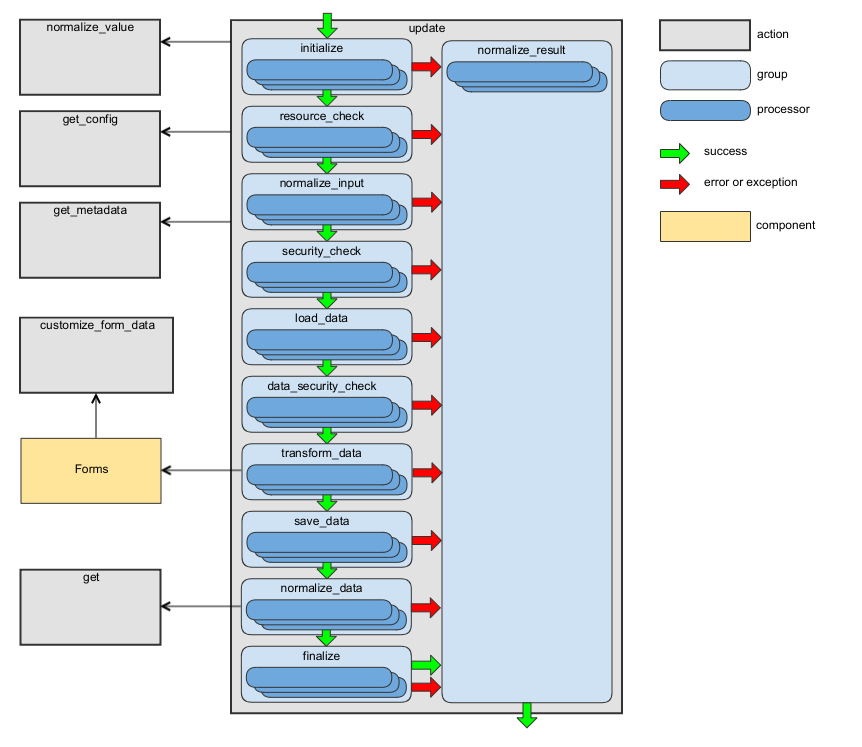
See the handleUpdate method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
update_list Action
This action is intended to create or update the list of entities of the same type.
The action works as an asynchronous operation. The result of this action is the initial status of the created
asynchronous operation and the Content-Location response header that contains an URL of API resource
of this operation.
The action is disabled by default. See Batch API documentation for details on enabling it for an API resource.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_list.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}.
The HTTP method for REST API: PATCH.
The context class: UpdateListContext. See Context class for more details.
The main processor class: UpdateListProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.update_list.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug update_list to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource is granted. |
When you add a new processor to the security_check group of the get action, add it to this group as well. This is necessary because the VIEW permission is checked here: the updated entity should be returned in the response, and the security_check group of the get action is disabled by the oro_api.load_normalized_entity processor. |
load_data |
Loading a request data to the storage. |
– |
save_data |
Creating an asynchronous batch operation. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
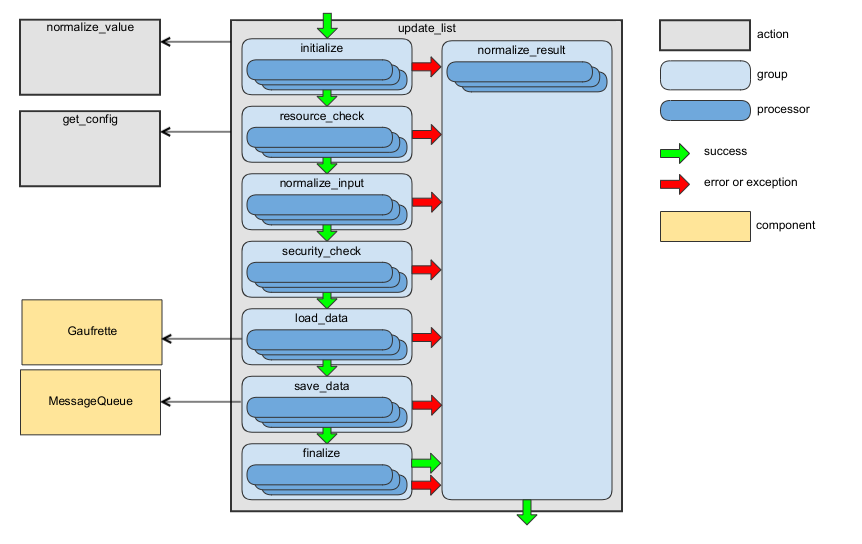
See the handleUpdateList method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
get_subresource Action
This action retrieves an entity (for the “to-one” relationship) or a list of entities (for the “to-many” relationship) connected to the entity by a given association. For more details, see the Fetching Resources section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_subresource.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: GET.
The context class: GetSubresourceContext. Also see SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: GetSubresourceProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.get_subresource.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug get_subresource to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
build_query |
Building a query to use to load data. |
– |
load_data |
Loading data. |
Use the customize_loaded_data action to modify loaded data. |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
normalize_data |
Converting the loaded data into an array. |
In most cases, the processors from this group are skipped because the EntitySerializer loads most entities and returns already normalized data. For details see LoadEntityByEntitySerializer and LoadEntitiesByEntitySerializer. |
finalize |
Final validation of the loaded data and adding the required response headers |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
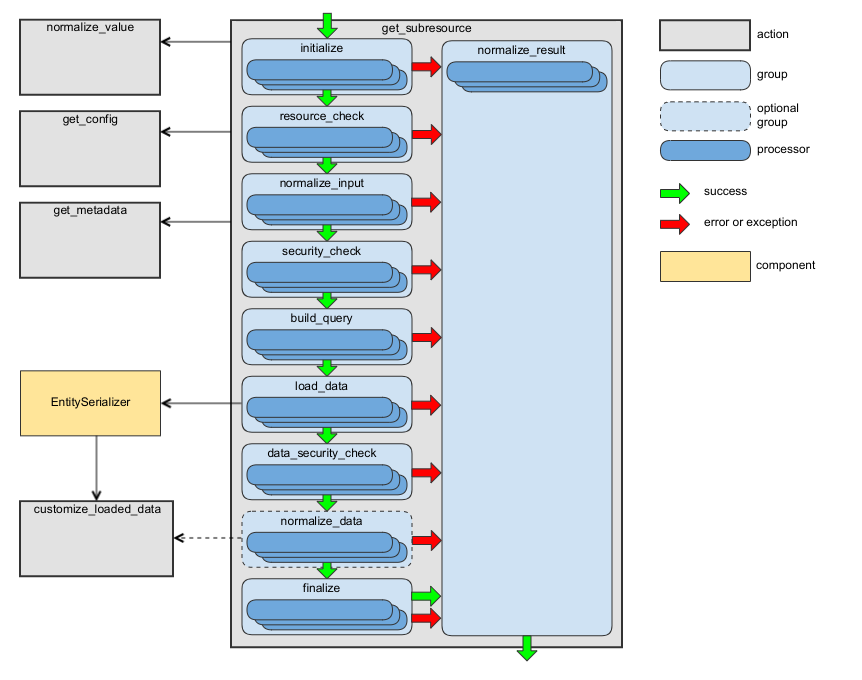
See the handleGetSubresource method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
update_subresource Action
Updates an entity or entities (depending on the association type) connected to an entity to which the sub-resource belongs. As this action does not have a default implementation, additional processors should be added, at least a processor that will build a form builder for your sub-resource. Take a look at BuildFormBuilder and BuildCollectionFormBuilder as examples of such processors. Use the request_target_class configuration option when request data are different from response data. Use the request_documentation_action configuration option when the request data documentation is different from the response data documentation.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_subresource.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: PATCH.
The context class: ChangeSubresourceContext. See the SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: ChangeSubresourceProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.change_subresource.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug update_subresource to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading an entity object to be updated. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
Use the customize_form_data action to modify and validate submitted data, and entities to be persisted into the database. |
normalize_data |
Converting the resulting entity into an array. |
– |
finalize |
Final validation of the loaded data. Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
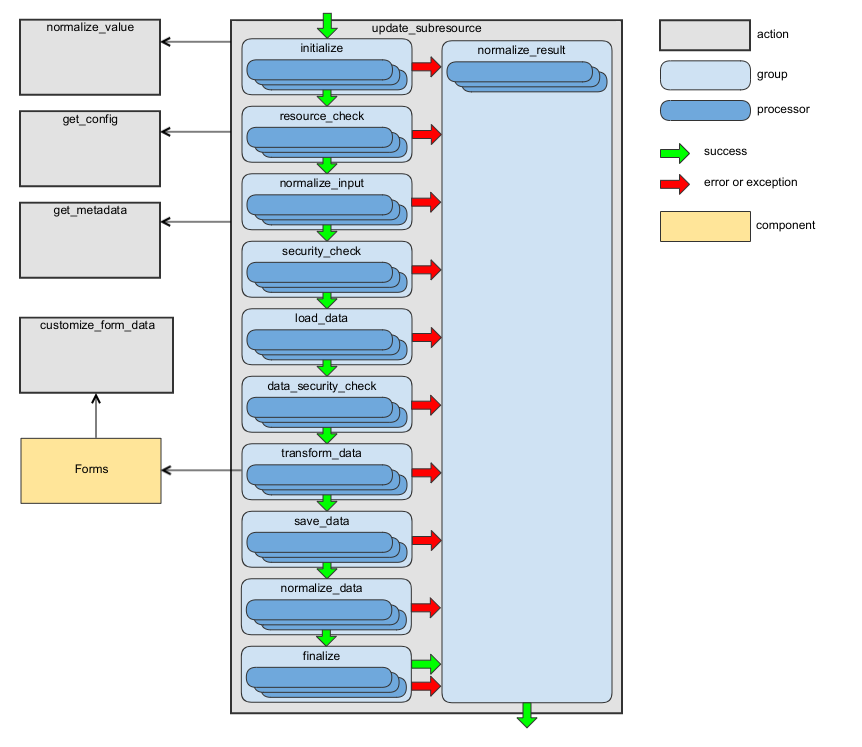
See the handleUpdateSubresource method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
Below is an example of registering a processor to build a form builder:
acme.api.items.build_form_builder:
class: Oro\Bundle\ApiBundle\Processor\Subresource\ChangeSubresource\BuildFormBuilder
arguments:
- '@oro_api.form_helper'
tags:
- { name: oro.api.processor, action: update_subresource, group: transform_data, association: items, parentClass: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Entity\ShoppingList, priority: 100 }
add_subresource Action
Adds an entity or entities (depending on the association type) connected to an entity to which the sub-resource belongs. As this action does not have a default implementation, additional processors should be added, at least a processor that will build a form builder for your sub-resource. Take a look at BuildFormBuilder and BuildCollectionFormBuilder as examples of such processors. Use the request_target_class configuration option when request data are different from response data. Use the request_documentation_action configuration option when the request data documentation is different from the response data documentation.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_subresource.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: POST.
The context class: ChangeSubresourceContext. See the SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: ChangeSubresourceProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.change_subresource.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug add_subresource to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading an entity object to be updated. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
Use the customize_form_data action to modify and validate submitted data, and entities to be persisted into the database. |
normalize_data |
Converting the resulting entity into an array. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
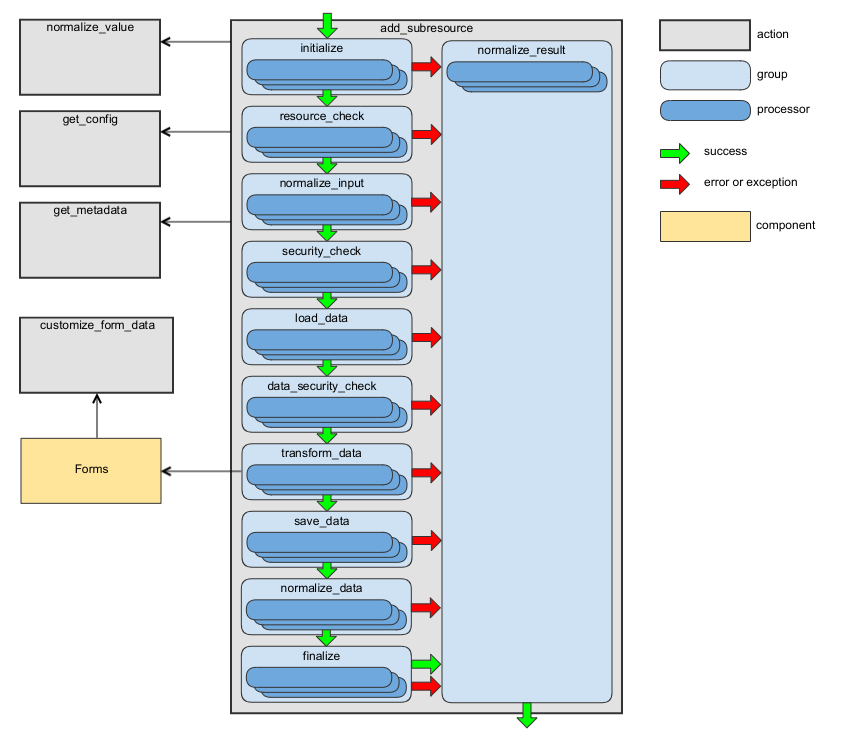
See the handleAddSubresource method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
Below is an example of registering a processor to build a form builder:
acme.api.items.build_form_builder:
class: Oro\Bundle\ApiBundle\Processor\Subresource\ChangeSubresource\BuildFormBuilder
arguments:
- '@oro_api.form_helper'
tags:
- { name: oro.api.processor, action: add_subresource, group: transform_data, association: items, parentClass: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Entity\ShoppingList, priority: 100 }
delete_subresource Action
Deletes an entity or entities (depending on the association type) connected to an entity to which the sub-resource belongs. As this action does not have a default implementation, additional processors should be added, at least a processor that will build a form builder for your sub-resource. Take a look at BuildFormBuilder and BuildCollectionFormBuilder as examples of such processors. Use the request_target_class configuration option when request data are different from response data. Use the request_documentation_action configuration option when the request data documentation is different from the response data documentation.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_subresource.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: DELETE.
The context class: ChangeSubresourceContext. See the SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: ChangeSubresourceProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.change_subresource.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug delete_subresource to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading an entity object to be updated. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
Use the customize_form_data action to modify and validate submitted data, and entities to be persisted into the database. |
normalize_data |
Converting the resulting entity into an array. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
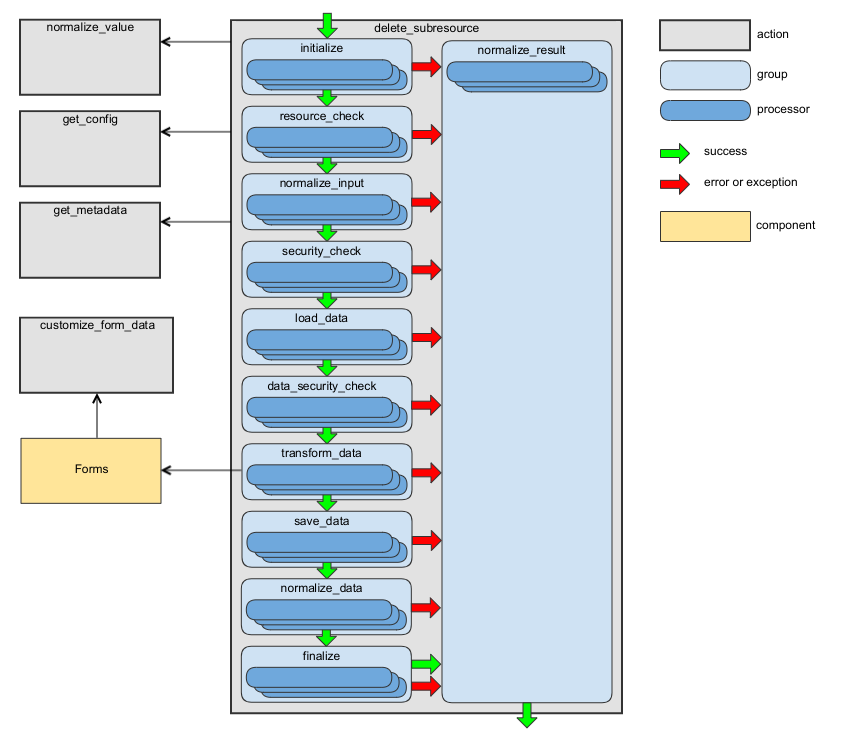
See the handleDeleteSubresource method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
Below is an example of registering a processor to build a form builder:
acme.api.items.build_form_builder:
class: Oro\Bundle\ApiBundle\Processor\Subresource\ChangeSubresource\BuildFormBuilder
arguments:
- '@oro_api.form_helper'
tags:
- { name: oro.api.processor, action: delete_subresource, group: transform_data, association: items, parentClass: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Entity\ShoppingList, priority: 100 }
get_relationship Action
This action retrieves an entity identifier (for the “to-one” relationship) or a list of entities’ identifiers (for the “to-many” relationship) connected to the entity by a given association. For more details, see the Fetching Relationships section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_relationship.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/relationships/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: GET.
The context class: GetRelationshipContext. Also see SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: GetRelationshipProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.get_relationship.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug get_relationship to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
build_query |
Building a query to use to load data. |
– |
load_data |
Loading data. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
normalize_data |
Converting loaded data into an array. |
In most cases, the processors from this group are skipped because the EntitySerializer loads most entities and returns already normalized data. For details see LoadEntityByEntitySerializer and LoadEntitiesByEntitySerializer. |
finalize |
Final validation of the loaded data and adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
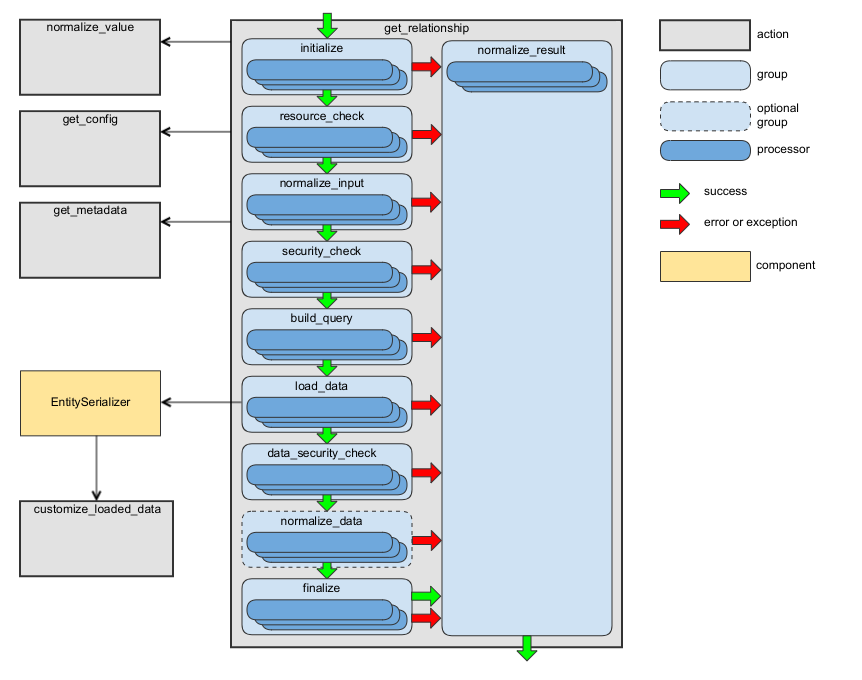
See the handleGetRelationship method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
update_relationship Action
This action changes an entity (for the “to-one” relationship) or completely replaces all entities (for the “to-many” relationship) connected to a given entity by a given association. For more details, see the Updating Relationships section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_relationship.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/relationships/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: PATCH.
The context class: UpdateRelationshipContext. Also see SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: UpdateRelationshipProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.update_relationship.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug update_relationship to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading an entity object to be updated. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
– |
normalize_data |
Converting the resulting relationship into an array. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
See the handleUpdateRelationship method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
add_relationship Action
This action adds one or several entities to a “to-many” relationship. For more details, see the Updating Relationships section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_relationship.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/relationships/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: POST.
The context class: AddRelationshipContext. See the SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: AddRelationshipProcessor
Existing worker processors: processors.add_relationship.yml, processors.shared.yml or run php bin/console oro:api:debug add_relationship.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading an entity object to be updated. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
– |
normalize_data |
Converting the resulting relationship into an array. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
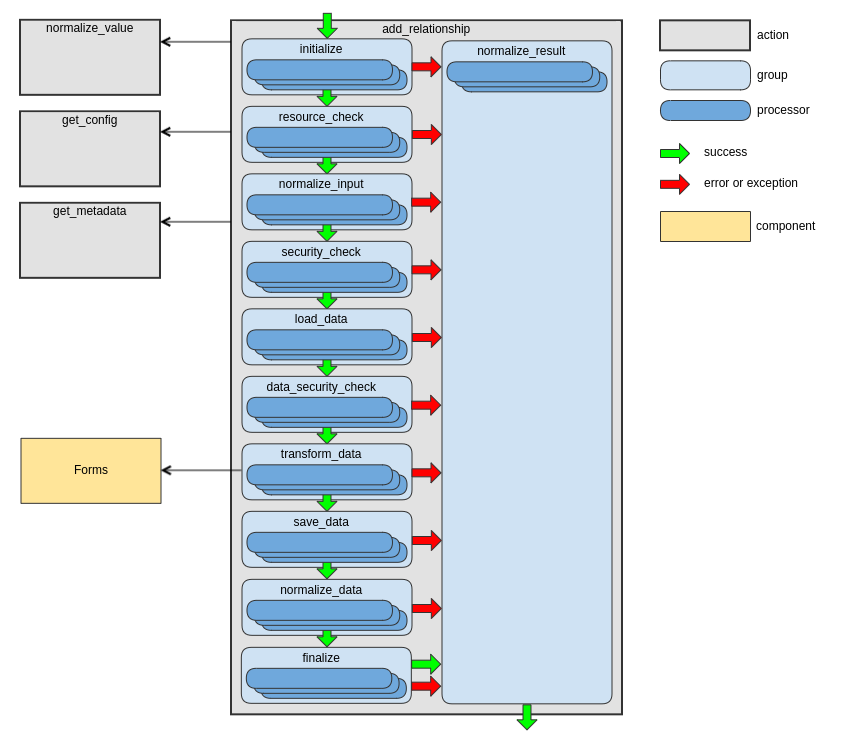
See the handleAddRelationship method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
delete_relationship Action
This action removes one or several entities from a “to-many” relationship. For more details, see the Updating Relationships section of the JSON:API specification.
The route name for REST API: oro_rest_api_relationship.
The URL template for REST API: /api/{entity}/{id}/relationships/{association}.
The HTTP method for REST API: POST.
The context class: AddRelationshipContext. See the SubresourceContext class for more details.
The main processor class: AddRelationshipProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.delete_relationship.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug delete_relationship to display the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API. |
– |
normalize_input |
Preparing the input data to be used by processors from the next groups. |
– |
security_check |
Checking whether access to the requested resource type is granted. |
– |
load_data |
Loading an entity object to be updated. |
– |
data_security_check |
Checking whether access to the loaded data is granted. |
– |
transform_data |
Building a Symfony Form and using it to transform and validate the request data. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting an entity. |
– |
normalize_data |
Converting the resulting relationship into an array. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
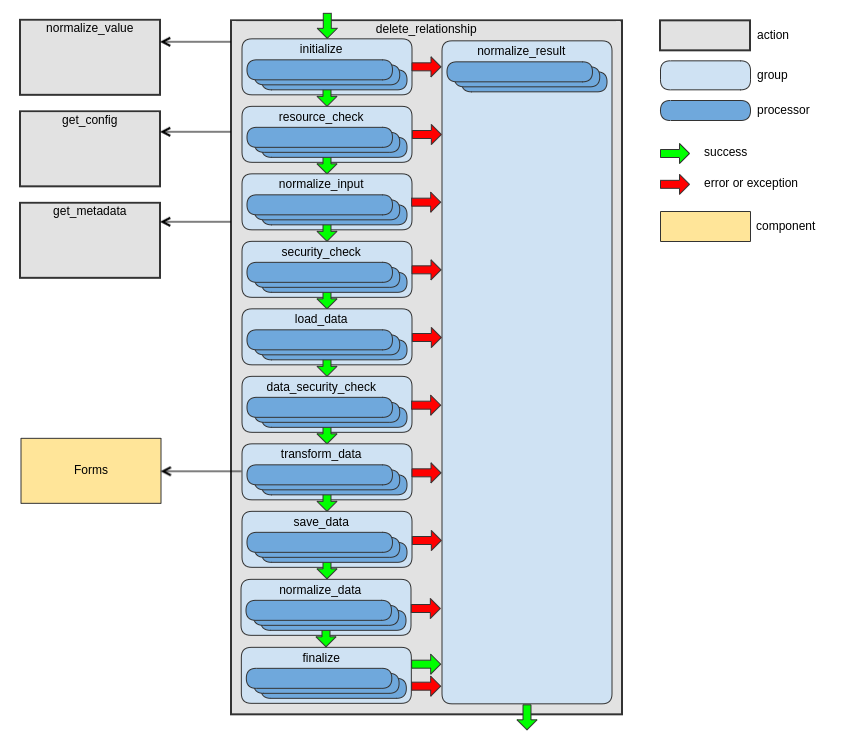
See the handleDeleteRelationship method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
options Action
This action retrieves the communication options for a resource. For more details, see the OPTIONS section of the HTTP specification.
This action is also intended CORS preflight requests for REST API. For more details, see the CORS Configuration section.
The HTTP method for REST API: OPTIONS.
The context class: OptionsContext.
The main processor class: OptionsProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.options.yml, processors.shared.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug options to list the processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
Processors from this group are executed during the generation of the API documentation. |
resource_check |
Checking whether the requested resource type is accessible via API and validating the request parameters. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
See the handleOptionsItem, handleOptionsList, handleOptionsSubresource and handleOptionsRelationship methods of RequestActionHandler as examples.
Auxiliary Actions
customize_loaded_data Action
This action makes modifications to the data loaded by the get, get_list and get_subresource actions.
The context class: CustomizeLoadedDataContext.
The main processor class: CustomizeLoadedDataProcessor.
An example of a processor used to modify the loaded data is ComputePrimaryField or Add a Computed Field. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug customize_loaded_data to display other processors registered in this action.
The collection tag attribute can be used for processors of this action to process all primary entities in get_list or get_subresource actions or all entities in to-many associations for get, get_list or get_subresource actions. An example of a case when using this attribute can be helpful if you want to execute one SQL query for all entities in a collection to get additional data instead of executing a separate SQL query for each entity in a collection. The default value the collection tag attribute is false. An example of a processor that should be executed to a whole collection:
services:
acme.api.process_my_collection:
class: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Api\Processor\ProcessMyCollection
tags:
- { name: oro.api.processor, action: customize_loaded_data, collection: true, class: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Entity\MyEntity }
Important
The collection elements are an associative array, and processors responsible for customizing the collection must keep keys in this array without changes.
Note
All processors for this action have the identifier_only tag attribute set to false. It means that such processors are not executed when loading relationships. If your processor should be executed when loading the relationships, set the identifier_only tag attribute to true. If your processor should be executed when loading relationships, primary, and included entities, set the identifier_only tag attribute to null. For example:
services:
acme.api.compute_my_field:
class: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Api\Processor\ComputeMyField
tags:
- { name: oro.api.processor, action: customize_loaded_data, identifier_only: true, class: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Entity\MyEntity }
Note
The identifier_only tag attribute is not supported if the collection tag attribute equals true. All processors intended to modify collections are executed when loading primary entities and entities in to-many associations, even if only the identifier field is requested.
Note
The ValueTransformer can be used in customize_loaded_data processors to convert a value to a format suitable for the API response.
customize_form_data Action
Makes modification and validation of submitted data, and entities to be persisted in the database by the create, update, update_relationship, add_relationship and delete_relationship actions.
The context class: CustomizeFormDataContext.
The main processor class: CustomizeFormDataProcessor.
This action is executed when the following Events are dispatched:
Event Name |
Description |
|---|---|
pre_submit |
This event is dispatched at the beginning of the Form::submit() method. |
submit |
This event is dispatched after the Form::submit() method has submitted and mapped the children, and after reverse transformation to normalized representation. |
post_submit |
This event is dispatched at the very end of the Form::submit(). |
pre_validate |
This event is dispatched at the end of the form submitting process, just before data validation. It can be used to final form data correcting after all listeners, except data validation listener, are executed and all relationships between submitted data are set. |
post_validate |
This event is dispatched at the end of the form submitting process, just after data validation. It can be used to finalize the form after all listeners, including the data validation listener, are executed. E.g. it can be used to correct form validation result. |
pre_flush_data |
This event is dispatched after the database transaction is open but before data are flushed into the database. Do not call EntityManager::persist() and EntityManager::remove() during handling of this event, use addAdditionalEntity() and addAdditionalEntityToRemove() methods of the context instead. |
post_flush_data |
This event is dispatched after data are successfully flushed into the database but before the database transaction is committed. |
post_save_data |
This event is dispatched after data are successfully flushed into the database, and the database transaction is committed. It can be used to perform some not crucial operations after data are saved into the database. It means that failure of these operations will not roll back data saved into the database. |
rollback_validated_request |
This event is dispatched before the database transaction is rolled back for API requests with a meta validate operation flag. |
Note
All these events use the same context, so it can be used to share data between events.
Note
When a request contains included entities, these events are dispatched for the included entities first and then for the primary entity. Each entity has its own context. Use the getSharedData() method of the Context class to share data between events for different entities.
An example of a processor used to modify the submitted data is MapPrimaryField. You can also run php bin/console oro:api:debug customize_form_data to display other processors registered in this action.
get_config Action
This action retrieves a configuration of an entity.
The context class: ConfigContext.
The main processor class: ConfigProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.get_config.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug get_config to see the list of processors.
Additionally, ConfigProvider was created to make usage of this action as easy as possible.
Example:
/** @var ConfigProvider $configProvider */
$configProvider = $container->get('oro_api.config_provider');
$config = $configProvider->getConfig($entityClassName, $version, $requestType, $configExtras);
get_metadata Action
This action retrieves the metadata of an entity.
The context class: MetadataContext.
The main processor class: MetadataProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.get_metadata.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug get_metadata to see the list of processors.
Additionally, MetadataProvider was created to make usage of this action as easy as possible.
Example:
/** @var MetadataProvider $metadataProvider */
$metadataProvider = $container->get('oro_api.metadata_provider');
$metadata = $metadataProvider->getMetadata($entityClassName, $version, $requestType, $entityConfig, $metadataExtras);
normalize_value Action
This action converts an input value to a requested data type.
The context class: NormalizeValueContext.
The main processor class: NormalizeValueProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.normalize_value.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug normalize_value to see the list of processors.
Additionally, ValueNormalizer and ValueNormalizerUtil were created to make usage of this action as easy as possible.
Example:
/** @var ValueNormalizer $valueNormalizer */
$valueNormalizer = $container->get('oro_api.metadata_provider');
$normalizedValue = $valueNormalizer->normalizeValue($value, $dataType, $requestType);
Note
The ValueNormalizer is intended to process input values only. In case you need to convert a value for the API response, use ValueTransformer.
collect_resources Action
This action gets a list of all resources accessible via the API.
The context class: CollectResourcesContext.
The main processor class: CollectResourcesProcessor.
Existing worker processors:processors.collect_resources.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug collect_resources to see the list of processors.
Additionally, ResourcesProvider was created to make it as easy as possible to use this action.
Example:
/** @var ResourcesProvider $resourcesProvider */
$resourcesProvider = $container->get('oro_api.resources_provider');
// get all API resources
// (all resources are configured to be used in API, including not accessible resources)
$resources = $resourcesProvider->getResources($version, $requestType);
// get class names of all API resources accessible through API
$accessibleResources = $resourcesProvider->getAccessibleResources($version, $requestType);
// check whether an entity is configured to be used in API
$isKnown = $resourcesProvider->isResourceKnown($entityClass, $version, $requestType);
// check whether an entity is accessible through API
$isAccessible = $resourcesProvider->isResourceAccessible($entityClass, $version, $requestType);
// check whether an entity is accessible as an association in API
$isAccessibleAsAssociation = $resourcesProvider->isResourceAccessibleAsAssociation($entityClass, $version, $requestType);
// check whether an entity does not have an identifier field
$isResourceWithoutIdentifier = $resourcesProvider->isResourceWithoutIdentifier($entityClass, $version, $requestType);
collect_subresources Action
This action retrieves a list of all sub-resources accessible via the API for a given entity type.
The context class: CollectSubresourcesContext.
The main processor class: CollectSubresourcesProcessor.
Existing worker processors: processors.collect_subresources.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug collect_subresources to see the list of processors.
Additionally, SubresourcesProvider was created to make usage of this action as easy as possible.
Example:
/** @var SubresourcesProvider $subresourcesProvider */
$subresourcesProvider = $container->get('oro_api.subresources_provider');
// get all sub-resources for a given entity
$entitySubresources = $subresourcesProvider->getSubresources($entityClass, $version, $requestType);
not_allowed Action
This action builds a response for the case when a request does not match any public action. An example of such a case can be a REST API request with an unsupported HTTP method.
This action does not have its own context and processor classes. It can work with any context class based on Context class, and any public action processor can process it. The processor to be used depends on the request attributes.
Run php bin/console oro:api:debug not_allowed to list the processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
– |
build_response |
Building the action response body, if the current request type requires it. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
See the handleNotAllowedItem, handleNotAllowedList, handleNotAllowedSubresource and handleNotAllowedRelationship methods of RequestActionHandler as examples.
unhandled_error Action
This action builds a response for the case when an unexpected error happens before any public action is started.
The context class: this action does not have its own context class, and it uses the Context class.
The main processor class: UnhandledErrorProcessor.
Run php bin/console oro:api:debug unhandled_error to list the processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see NormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
See the handleUnhandledError method of RequestActionHandler as an example.
batch_update Action
This action updates or creates a set of entities of the same type that are part of an asynchronous batch operation. It is triggered by the update_list action.
The context class: BatchUpdateContext.
The main processor class: BatchUpdateProcessor.
Existing worker processors:processors.batch_update.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug batch_update to see the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
– |
finalize |
Adding the required response headers. |
– |
save_data |
Persisting entities. |
– |
save_errors |
Persisting found errors. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see ByStepNormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
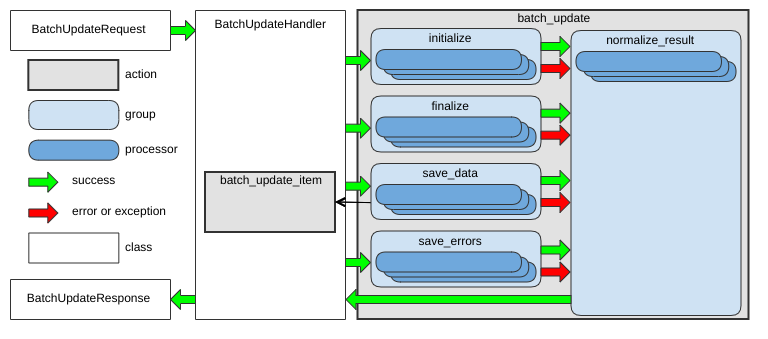
See BatchUpdateHandler as an example.
batch_update_item Action
This action creates or updates an entity that is part of an asynchronous batch operation. It is used by the batch_update action.
The context class: BatchUpdateItemContext.
The main processor class: BatchUpdateItemProcessor.
Existing worker processors:processors.batch_update_item.yml. Run php bin/console oro:api:debug batch_update_item to see the list of processors.
This action has the following processor groups:
Group Name |
Responsibility of Processors |
Description |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
Context initialization. |
– |
transform_data |
Converts the request data to entity object. |
– |
normalize_result |
Building the action result. |
The processors from this group are executed even if a processor from previous groups throws an exception. For implementation details, see ByStepNormalizeResultActionProcessor. |
The following diagram shows the main data flow for this action:
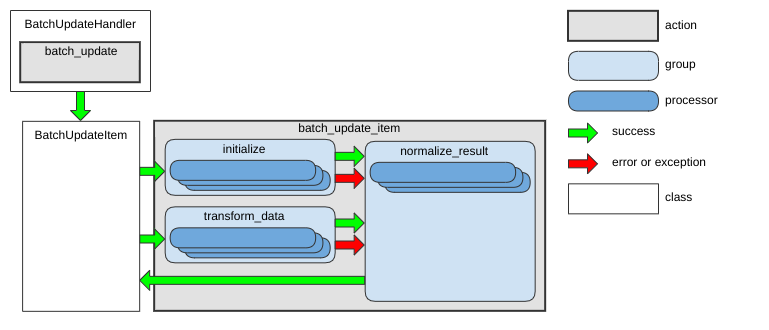
See BatchUpdateItem as an example.
Context Class
The Context class is used as a superclass for the context classes of CRUD actions such as get, get_list, create, update, delete, and delete_list.
General methods:
getClassName() - Retrieves the fully-qualified class name of an entity.
setClassName(className) - Sets fully-qualified class name of an entity.
getRequestHeaders() - Retrieves the request headers.
setRequestHeaders(parameterBag) - Sets an object to use for accessing the request headers.
getResponseHeaders() - Retrieves the response headers.
setResponseHeaders(parameterBag) - Sets an object to use for accessing accessing the response headers.
getResponseStatusCode() - Retrieves the response status code.
setResponseStatusCode(statusCode) - Sets the response status code.
isSuccessResponse() - Indicates whether a result document represents a success response.
getResponseDocumentBuilder() - Retrieves the response document builder.
setResponseDocumentBuilder(documentBuilder) - Sets the response document builder.
getFilters() - Retrieves a list of filters to set additional restrictions to a query used to retrieve the entity data.
getFilterValues() - Retrieves a collection of the FilterValue objects that contains all incoming filters.
setFilterValues(accessor) - Sets an object to use for accessing the incoming filters.
isMainRequest() - Indicates whether the current action processes a main API request or is executed as part of another action.
setMainRequest(main) - Sets a flag that indicates the current action processes a main API request or is executed as part of another action.
isCorsRequest() - Indicates whether the current request is CORS request.
setCorsRequest(cors) - Sets a flag indicates whether the current request is CORS request.
isHateoasEnabled() - Indicates whether HATEOAS is enabled.
setHateoas(flag) - Sets a flag indicates whether HATEOAS is enabled.
hasQuery() - Checks whether a query used to get the result data exists.
getQuery() - Retrieves a query used to get result data.
setQuery(query) - Sets a query used to get result data.
getCriteria() - Retrieves the Criteria object that sets additional restrictions to a query used to retrieve the entity data.
setCriteria(criteria) - Sets the Criteria object that sets additional restrictions to a query used to retrieve the result data.
getAllEntities(primaryOnly = false) - Gets all entities, primary and included ones, that are processing by an action.
hasErrors() - Checks whether any error happened when processing an action.
getErrors() - Retrieves all errors that occurred during the processing of an action.
addError(error) - Registers an errors.
resetErrors() - Removes all errors.
isSoftErrorsHandling() - Retrieves a value that indicates whether to stop the further processing or throw an exception in case of error.
setSoftErrorsHandling(softErrorsHandling) - Sets a value that indicates whether to stop the further processing or throw an exception in case of error.
setProcessed(operationName) - Marks work as done. In most cases, this method is unnecessary because it is easy to determine when work is already complete by checking the state of a context. However, if a processor performs complex work, it might be required to mark it as already done directly.
clearProcessed(operationName) - Marks work as not yet done.
isProcessed(operationName) - Checks whether work is already done.
getSharedData() - Retrieves an object used to share data between a primary action and actions executed as part of this action. Also, this object can be used to share data among different kinds of child actions.
setSharedData(parameterBag) - Sets an object used to share data.
getNormalizationContext() - Gets a context for response data normalization.
getInfoRecords() - Gets a list of records containing additional information about collections, e.g., the “has_more” flag in such a record indicates whether a collection has more records than was requested.
setInfoRecords(infoRecords) - Sets a list of records containing additional information about collections, e.g., the “has_more” flag in such a record indicates whether a collection has more records than was requested.
addInfoRecord(key, value) - Adds a record that contains an additional information about collections.
addAssociationInfoRecords(propertyPath, infoRecords) - Adds records that contain an additional information about a collection valued association.
getNotResolvedIdentifiers() - Gets all not resolved identifiers.
addNotResolvedIdentifier(path, identifier) - Adds an identifier that cannot be resolved.
removeNotResolvedIdentifier(path) - Removes an identifier that cannot be resolved.
Entity configuration-related methods:
getConfigExtras() - Retrieves a list of requests for configuration data.
setConfigExtras(extras) - Sets a list of requests for configuration data.
hasConfigExtra(extraName) - Checks whether some configuration data is requested.
getConfigExtra(extraName) - Retrieves a request for configuration data by its name.
addConfigExtra(extra) - Adds a request for some configuration data.
removeConfigExtra(extraName) - Removes a request for some configuration data.
getConfigSections() - Retrieves names of all requested configuration sections.
hasConfig() - Checks whether a configuration of an entity exists.
getConfig() - Retrieves a configuration of an entity.
setConfig(config) - Sets a custom configuration of an entity. This method can be used to override the default configuration of an entity completely.
hasConfigOfFilters(initialize) - Checks whether an entity has a configuration of filters.
getConfigOfFilters() - Retrieves a configuration of filters for an entity.
setConfigOfFilters(config) - Sets a custom configuration of filters. This method can be used to override the default configuration of filters completely.
hasConfigOfSorters(initialize) - Checks whether an entity has a configuration of sorters.
getConfigOfSorters() - Retrieves a configuration of sorters for an entity.
setConfigOfSorters(config) - Sets a custom configuration of sorters. This method can be used to override the default configuration of sorters completely.
hasConfigOf(configSection, initialize) - Checks whether a configuration of the given section exists.
getConfigOf(configSection) - Retrieves a configuration from the given section.
setConfigOf(configSection, config) - Sets a configuration for the given section. This method can be used to override the default configuration for the given section completely.
Entity metadata-related methods:
hasIdentifierFields() - Checks whether metadata of an entity has at least one identifier field.
getMetadataExtras() - Retrieves a list of requests for additional metadata info.
setMetadataExtras(extras) - Sets a list of requests for additional metadata info.
hasMetadataExtra() - Checks whether some additional metadata info is requested.
addMetadataExtra(extra) - Adds a request for some additional metadata info.
removeMetadataExtra(extraName) - Removes a request for some additional metadata info.
hasMetadata() - Checks whether metadata of an entity exists.
getMetadata() - Retrieves metadata of an entity.
setMetadata(metadata) - Sets metadata of an entity. This method can be used to override the default metadata of an entity completely.
SubresourceContext Class
The SubresourceContext class is used as a superclass for the context classes of sub-resources related actions such as get_subresource, get_relationship, update_relationship, add_relationship and delete_relationship. This class provides methods to work with parent entities in addition to the Context class.
General methods:
getParentClassName() - Retrieves the fully-qualified class name of the parent entity.
setParentClassName(className) - Sets fully-qualified class name of the parent entity.
getParentId() - Retrieves an identifier of the parent entity.
setParentId(parentId) - Sets an identifier of the parent entity.
getAssociationName() - Retrieves an association name that represents a relationship.
setAssociationName(associationName) - Sets an association name that represents a relationship.
isCollection() - Indicates an association that represents the “to-many” or “to-one” relationship.
setIsCollection(value) - Sets a flag that indicates whether an association represents “to-many” or “to-one” relationship.
hasParentEntity() - Checks whether the parent entity exists in the context.
getParentEntity() - Retrieves the parent entity object.
setParentEntity(parentEntity) - Sets the parent entity object.
Parent entity configuration-related methods:
getParentConfigExtras() - Retrieves a list of requests for configuration data for the parent entity.
setParentConfigExtras(extras) - Sets a list of requests for configuration data for the parent entity.
hasParentConfig() - Checks whether a configuration of the parent entity exists.
getParentConfig() - Retrieves a configuration of the parent entity
setParentConfig(config) - Sets a custom configuration of the parent entity. This method can be used to completely override the default configuration of the parent entity.
Parent entity metadata-related methods:
getParentMetadataExtras() - Retrieves a list of requests for additional metadata info for the parent entity.
setParentMetadataExtras(extras) - Sets a list of requests for additional metadata info for the parent entity.
hasParentMetadata() - Checks whether metadata of the parent entity exists.
getParentMetadata() - Retrieves metadata of the parent entity.
setParentMetadata(metadata) - Sets metadata of the parent entity. This method can be used to override the default metadata of the parent entity completely.
Creating a New Action
To create a new action, to create two classes:
context - This class represents a context in the scope of which an action is executed. An instance of this class is used to store the input and output data and share data between processors. This class must extend ApiContext. Depending on your needs, you can use another classes derived from ApiContext, for example Context, SingleItemContext or ListContext.
main processor - This class is the main entry point for an action and is responsible for creating an instance of the context class and executing all worker processors. This class must extend ActionProcessor and implement the
createContextObjectmethod. Depending on your needs, you can use other classes derived from ActionProcessor, for example, NormalizeResultActionProcessor.
namespace Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Api\Processor;
use Oro\Bundle\ApiBundle\Processor\ApiContext;
class MyActionContext extends ApiContext
{
}
namespace Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Api\Processor;
use Oro\Component\ChainProcessor\ActionProcessor;
class MyActionProcessor extends ActionProcessor
{
#[\Override]
protected function createContextObject(): MyActionContext
{
return new MyActionContext();
}
}
Additionally, you need to register your processor in the dependency injection container:
acme.my_action.processor:
class: Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Api\Processor\MyActionProcessor
public: false
arguments:
- '@oro_api.processor_bag'
- my_action # the name of an action
If you need to create groups for your action, register them in the ApiBundle configuration. To do this, add Resources/config/oro/app.yml to your bundle, for example:
oro_api:
actions:
my_action:
processing_groups:
initialize:
priority: -10
load_data:
priority: -20
finalize:
priority: -30
Note
The priority attribute is used to control the order in which groups of processors are executed. The higher the priority, the earlier a group of processors is executed. The default value is 0. The possible range is from -254 to 252. For details on processor creation, see the Processors section.