Enable Entity Pagination
To enable entity pagination, add option entity_pagination to datagrid options. If this option is enabled, the session collects identifiers of entities on the first visit view or edit page of any entity from the specified grid and these identifiers are used to generate links to the previous and next entities on this page.
The datagrid must also have a column with the same name as the entity identifier field used to collect identifiers. View and edit page routes must have a parameter with the same name.
Example
Suppose that pagination must be enabled for the User entity with an identifier column called “id”.
The datagrid must have an
entity_paginationoption in the configuration:
The datagrid has an identifier column in the result:
The User view page route has an identifier column in route parameters:
#[Route(path: '/question', name: 'acme_demo_question_')]
class QuestionController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route(path: '/view/{id}', name: 'view', requirements: ['id' => '\d+'])]
public function viewAction(Question $entity): array
{
return [
'entity' => $entity,
];
}
}
System Configuration
Entity pagination has two system configuration options to handle the pagination process. These options are accessible in section System Configuration > General Setup > Display Settings > Data Grid Settings.
Record Pagination, default is true, key _oro_entity_pagination.enabled_ - used to enable or disable entity pagination across the system.
Record Pagination limit, default is 1000, key _oro_entity_pagination.limit_ - allows to set the maximum number of entities in the grid for entity pagination (i.e., if the number of entities in the grid is more than the limit, then entity pagination will be unavailable).
Backend Processing
When a user comes from the grid with enabled entity pagination to the view or edit pages, grid parameters (filters, sorters, etc.) are transmitted as URL parameters in the browser address bar. Then, the entity pagination storage data collector sends a query to get all records with these grid parameters considering ACL permissions (for example, edit ACL might be stricter than view).
There are two different scopes in the storage to collect data. One scope is used to collect view pagination entity identifiers, and the other is used to collect edit pagination entity identifiers. Next, the collector fills the view or edit scope storage depending on which page the user visited. If the limit of records count is more than Record Pagination limit collector set empty array for this scope. Next time if storage has data for the current scope for the current grid parameters, the collector will not send a request to get records.
After switching back to the datagrid, both storage scopes are cleared.
Entity pagination navigation has EntityPaginationController actions. Each action checks if the pagination identifier is available and accessible. A different user can delete some entities from the current scope during pagination over entities. When this happens, and another user navigates to this entity, they see the not_available message and then the next available entity. If the ACL permission for the entity in the current scope is changed and a user navigates to this entity, the message not_accessible is displayed. Unavailable or inaccessible entities are deleted from the storage, entity identifier count refreshes, and the message stats_number_view_%count% is displayed.
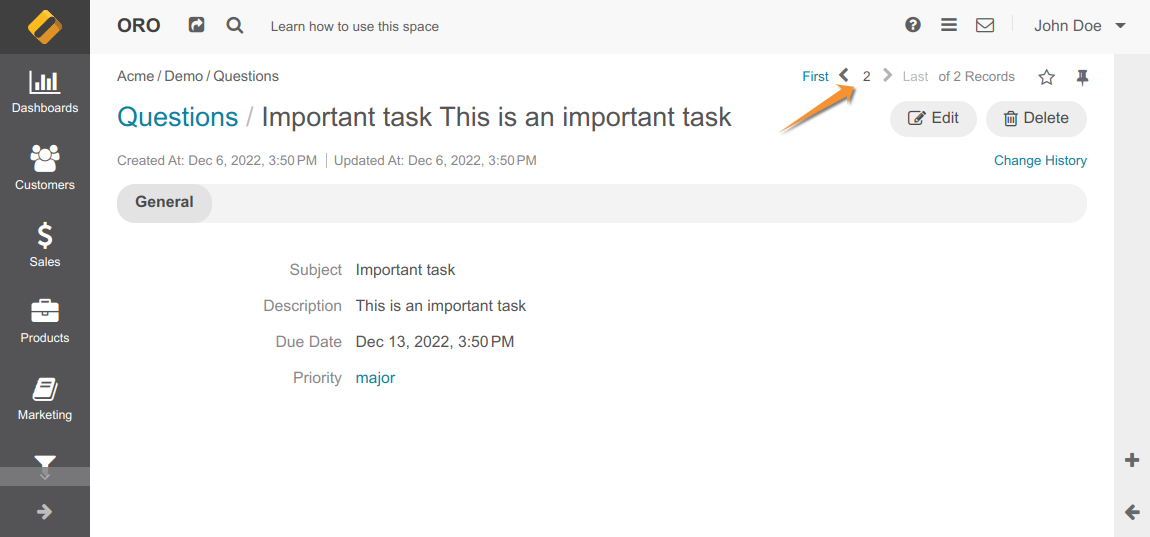
The default entity view has a placeholder used to add an entity pagination section. When a user arrives at the entity view page, this section shows pagination details (<M> of <N> entities, links to the first, previous, next, and last entities) extracted from the user session for the current entity type.