Emails
Database Diagram
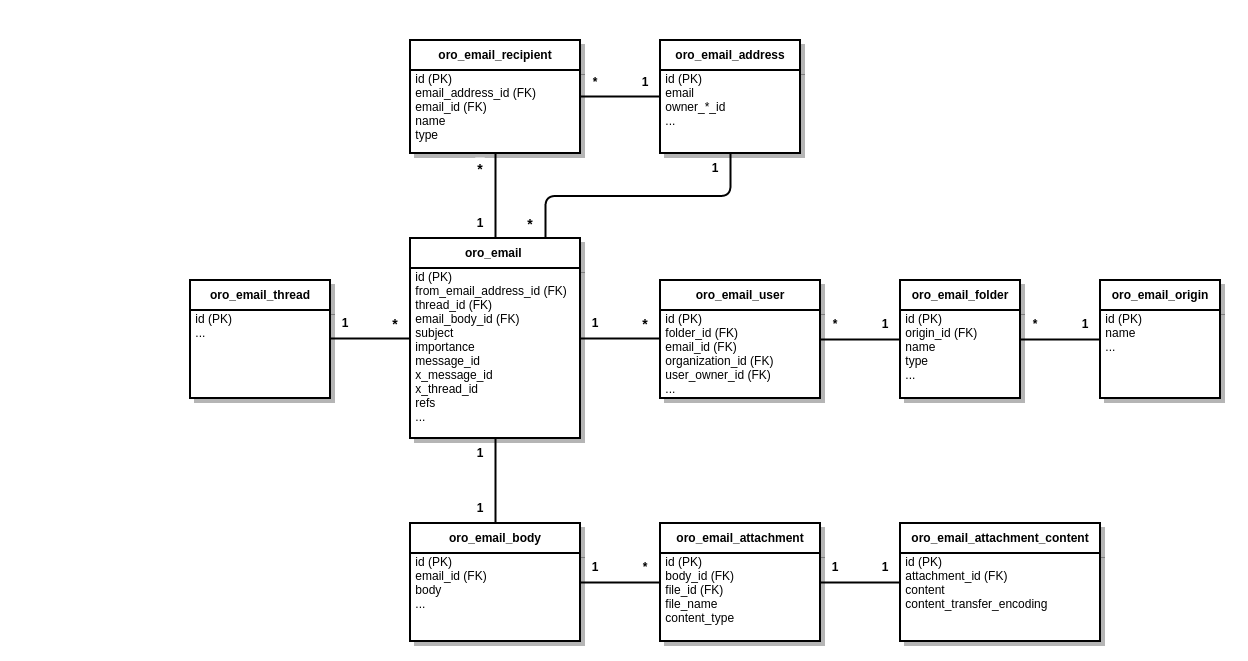
Email Address Owners
Each email address can be connected to an entity object which is the owner of this email address. An email address can have one and only one owner. User and Contact entities can own an email address, but other entities can be easily configured for this purpose. Let’s take a look at the changes made in OroUserBundle to allow the User entity to be the owner:
namespace Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity;
...
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Entity\EmailOwnerInterface;
class User extends AbstractUser implements
EmailOwnerInterface,
EmailHolderInterface,
FullNameInterface,
AdvancedApiUserInterface,
ExtendEntityInterface
{
...
}
namespace Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity;
...
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Entity\EmailInterface;
class Email implements EmailInterface
{
...
}
UserBundle/Entity/Provider/EmailOwnerProvider.php
namespace Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity\Provider;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Oro\Bundle\BatchBundle\ORM\Query\BufferedQueryResultIterator;
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Entity\EmailOwnerInterface;
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Entity\Provider\EmailOwnerProviderInterface;
use Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity\Email;
use Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity\User;
class EmailOwnerProvider implements EmailOwnerProviderInterface
{
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getEmailOwnerClass(): string
{
return User::class;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function findEmailOwner(EntityManagerInterface $em, string $email): ?EmailOwnerInterface
{
/** @var User|null $user */
$user = $em->getRepository(User::class)->findOneBy(['email' => $email]);
if (null === $user) {
/** @var Email|null $emailEntity */
$emailEntity = $em->getRepository(Email::class)->findOneBy(['email' => $email]);
if (null !== $emailEntity) {
$user = $emailEntity->getUser();
}
}
return $user;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getOrganizations(EntityManagerInterface $em, string $email): array
{
$result = [];
$rows = $em->createQueryBuilder()
->from(User::class, 'u')
->select('o.id')
->join('u.organizations', 'o')
->where('u.email = :email')
->setParameter('email', $email)
->getQuery()
->getArrayResult();
foreach ($rows as $row) {
$result[] = (int)$row['id'];
}
$rows = $em->createQueryBuilder()
->from(Email::class, 'ue')
->select('o.id')
->join('ue.user', 'u')
->join('u.organizations', 'o')
->where('ue.email = :email')
->setParameter('email', $email)
->getQuery()
->getArrayResult();
foreach ($rows as $row) {
$result[] = (int)$row['id'];
}
if ($result) {
$result = array_values(array_unique($result));
}
return $result;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getEmails(EntityManagerInterface $em, int $organizationId): iterable
{
$qb = $em->createQueryBuilder()
->from(User::class, 'u')
->select('u.email')
->where('u.organization = :organizationId')
->setParameter('organizationId', $organizationId)
->orderBy('u.id');
$iterator = new BufferedQueryResultIterator($qb);
foreach ($iterator as $row) {
yield $row['email'];
}
$qb = $em->createQueryBuilder()
->from(Email::class, 'ue')
->select('ue.email')
->join('ue.user', 'u')
->where('u.organization = :organizationId')
->setParameter('organizationId', $organizationId)
->orderBy('ue.id');
$iterator = new BufferedQueryResultIterator($qb);
foreach ($iterator as $row) {
yield $row['email'];
}
}
}
services:
oro_user.email.owner.provider:
class: Oro\Bundle\UserBundle\Entity\Provider\EmailOwnerProvider
tags:
- { name: oro_email.owner.provider, order: 1 }
The code blocks above illustrate the following steps to configure a new owner:
Implement EmailOwnerInterface in the entity which you wish to make an email address owner.
Implement EmailInterface in the entity responsible for storing emails.
Implement EmailOwnerProviderInterface in your bundle.
Register your email owner provider as a service and mark it by oro_email.owner.provider tag. The order attribute is optional and can be used to resolve ambiguity when several email address owners have the same email address. In this case, the owner with the lower value of the order attribute wins.
Before the system can work with your email address owner, you have to do two things:
Update the database schema using php bin/console doctrine:schema:update command. The new foreign key will be created in oro_email_address table.
Run php bin/console cache:warmup command to regenerate doctrine proxy class used to work with the EmailAddress entity. This class is located in the app/entities/Extend/Cache/OroEmailBundle/Entity directory.
Email Body and Attachments Loaders
Emails can be loaded from different sources, for example, using IMAP protocol or through Exchange Web Services. That is why we need a way to get the email body and attachments for already loaded emails. To add a new loader:
Create a class that implements EmailBodyLoaderInterface.
Register it in DI and mark it with
oro_email.email_body_loadertag.
For example:
namespace Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Email;
use Acme\Bundle\DemoBundle\Entity\SomeEmailOrigin;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManager;
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Entity\Email;
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Entity\EmailFolder;
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Entity\EmailOrigin;
use Oro\Bundle\EmailBundle\Provider\EmailBodyLoaderInterface;
class SomeEmailBodyLoader implements EmailBodyLoaderInterface
{
/**
* @inheritDoc
*/
public function supports(EmailOrigin $origin)
{
return $origin instanceof SomeEmailOrigin;
}
/**
* @inheritDoc
*/
public function loadEmailBody(EmailFolder $folder, Email $email, EntityManager $em)
{
// implementation
}
}
Key Classes
Below is a list of the key EmailBundle classes:
EmailEntityBuilder provides a way to build email-related entities. It is responsible for correctly building batches of email entities when you need to add many emails in one database transaction.
EntityCacheWarmer creates/removes a proxy class for the EmailAddress entity in the app/entities folder.
EmailAddressManager is responsible for the correct creation of a proxy object for the EmailAddress entity and allows to get the correct doctrine repository for this entity. This class must be used because EmailAddress is a doctrine-mapped superclass, and it cannot be created directly.
EmailOwnerManager is responsible for binding/unbinding EmailAddress to the correct owner. This class handles modifications of all entities, implements EmailOwnerInterface and EmailInterface, and makes the necessary changes in the
oro_email_addresstable.EmailOwnerProviderStorage holds all available email owner providers.
EmailOwnerProvider implements a chain of email owner providers.
EmailBodyLoaderInterface provides an interface for classes responsible for loading the email body and attachments from different email servers, such as IMAP.
EmailBodyLoaderSelector implements functionality to find appropriate email body and attachments loader.
AbstractEmailSynchronizer provides the base algorithm that can be used to synchronize emails from different mailboxes, such as IMAP. In the derived class, you need to implement two methods: getEmailOriginClass and createSynchronizationProcessor. You can check out an example of this in OroImapBundle/Sync/ImapEmailSynchronizer.php.
AbstractEmailSynchronizationProcessor is the base class for different email synchronization processors.
Email Flash Popup
You can add the tree below to the config.yml file and have the ability to set the maximum visible emails in a flash popup:
oro_email:
flash_notification:
max_emails_display: "%email_flash_max_emails_display%"
You can retrieve this parameter by using the command below:
$this->container->getParameter('oro_email.flash_notification.max_emails_display');