Important
We are updating the images for OroCommerce version 6.1 to align with the latest changes in the back-office design. During this transition, some images may still show older versions. Thank you for your patience as we work to update all visuals to reflect these changes.
Content Block Management Concept Guide
Content blocks are fractions of your web page or a piece of content that you create to be displayed on your website. When creating a landing page, you can enrich it with a variety of information, adding different types of content as individual content blocks (e.g., text, buttons, widgets, videos, images, or links). Each content block is an independent component that you can insert into one or several pages.
In Oro applications, content blocks are usually used when you need to reuse the same content fragment on multiple pages of your website, for instance, a company address.
With a powerful WYSIWYG editor, integrated into all content blocks, you can apply different formatting and styles to customize and personalize your content.
You can also specify the visibility restrictions for each content block or content variant by setting the target localization, website, customer, or customer group. This way, the content block will be displayed in the storefront only if the configuration is met.
For instance, one content block, named Company Address, can have the following multiple variants:
Your US company address that is restricted to the US website.
Your affiliate address in Germany, translated to German and restricted to the German website.
A request to register an account for all guest customers who visit your store, regardless of their localization.
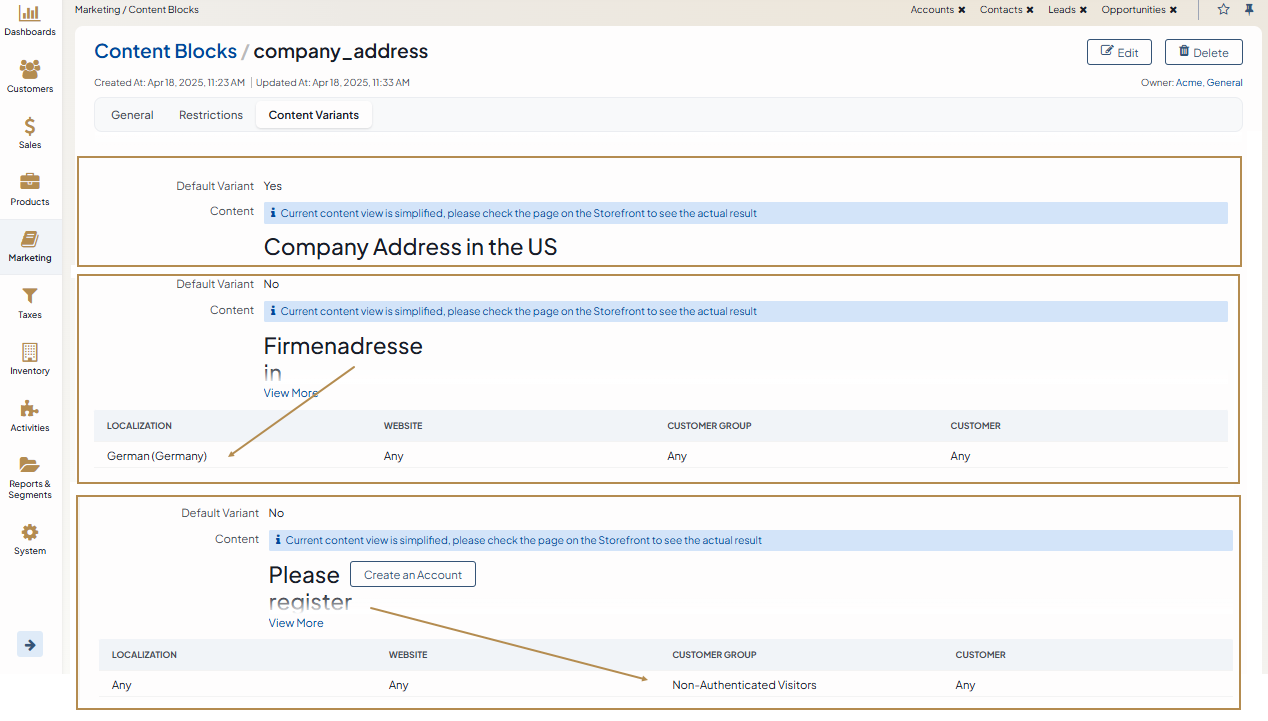
Depending on the restrictions that you configure for each content block variant, the related content is shown.
One of the benefits of using content blocks is the easy way to allocate them within the landing page once they are created. You just drag and drop the block into the required place, moving it with the cursor, if needed. If you are not satisfied with it, delete it and take a new one.
Hint
Check out the Manage Content Blocks in the Back-Office guide for more details on how to create content blocks, add variants, and translate them to the required language.